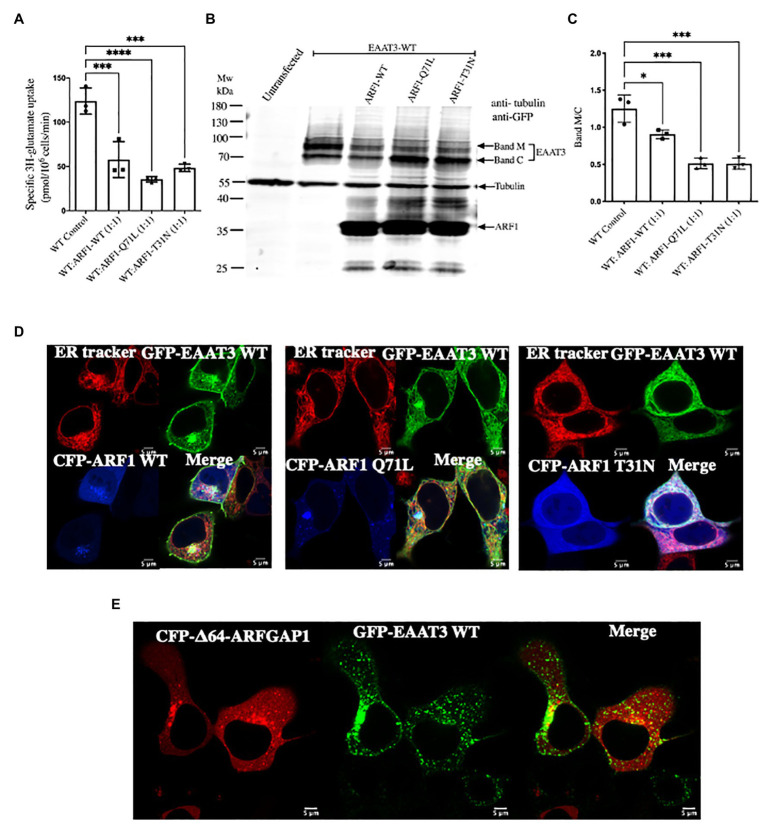
Figure 6.
Arresting coat protein I (COPI) vesicle formation prevents EAAT3 anterograde trafficking. (A) Impairment of uptake by EAAT3 upon arresting COPI by co-transfecting with GFP-EAAT3 and CFP-ARF1 WT or CFP-ARF1-Q71L/T31N. Data represents mean ± SD (n = 4); ***p = 0.0001, one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test; ***p = 0.0006 between EAAT3 WT Control and WT: ARF1 WT (1:1); ****p < 0.0001 between EAAT3-WT Control and WT: ARF1 Q71L (1:1); ***p = 0.0003 between EAAT3-WT Control and WT: ARF1 T31N (1:1). (B) Representative western blot analysis prepared from whole cell lysate depicting the loss of glycosylated surface expression of EAAT3 upon co-expression of CFP-ARF1-Q71L/T31N. Band M represents the mature glycosylated form of EAAT3 and band C represents the core glycosylated form of EAAT3. It should be noted that the GFP antibody recognizes CFP, such that exogenously expressed CFP-ARF1 WT and CFP-ARF1-Q71L/T31N were also detected. (C) Analysis of the protein band intensities and comparison of glycosylated vs. ER fraction of EAAT3. Data represents mean ± SD (n = 3); ****p < 0.0001; one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test; *p = 0.0124 between EAAT3-WT Control and WT: ARF1 WT (1:1); ***p = 0.0001 between EAAT3-WT Control and WT: ARF1 Q71L (1:1); ***p = 0.0001 between EAAT3 WT Control and WT: ARF1 T31N (1:1). (D) Confocal microscopy imaging of GFP-EAAT3 with CFP-ARF1 WT or CFP-ARF1 Q71L or CFP-ARF1-T31N shows restriction of EAAT3 within the ER upon co-expression of the ARF1 mutants. (E) Confocal microscopy imaging of GFP-EAAT3 with CFP-Δ64-ARFGAP1 depicting perinuclear punctate structure retention.