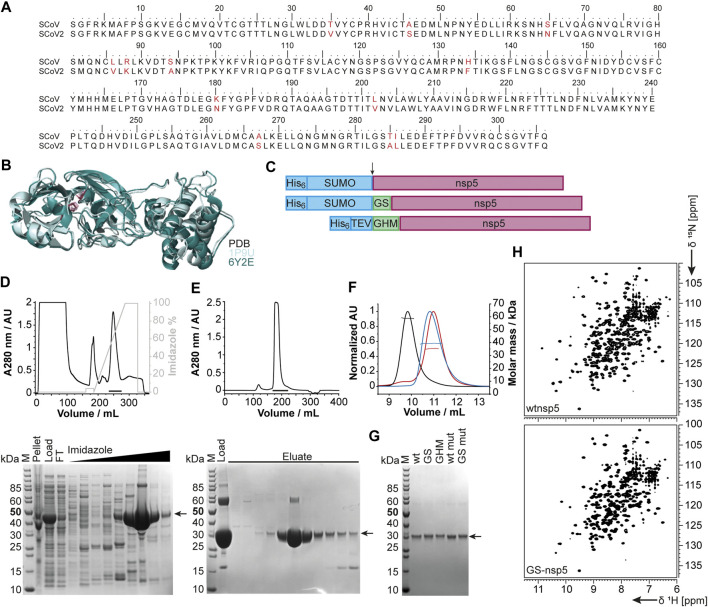
FIGURE 5.
Rationale of construct design, expression, and purification of different nsp5 constructs. (A) Sequence alignment of SCoV and SCoV2 fl nsp5. (B) X-ray structural overlay of the homologous SCoV (PDB 1P9U, light blue) and SCoV2 nsp5 (PDB 6Y2E, green) in cartoon representation. The catalytic dyad (H41 and C145) is shown in stick representation (magenta). (C) Schematics of nsp5 expression constructs involving purification and solubilization tags (blue), different N-termini and additional aa after cleavage (green), and nsp5 (magenta). Cleavage sites are indicated by an arrow. (D, E) An exemplary purification is shown for wtnsp5. IMAC (D) and SEC (E) chromatograms (upper panels) and the corresponding SDS PAGE (lower panels). Black bars in the chromatograms indicate pooled fractions. Gel samples are as follows: M: MW standard; pellet/load: pellet/supernatant after cell lysis; FT: IMAC flow-through; imidazole: eluted fractions with linear imidazole gradient; eluate: eluted SEC fractions from input (load). (F) SEC-MALS analysis with ∼0.5 µg of wtnsp5 without additional aa (wtnsp5, black) with GS (GS-nsp5, blue) and with GHM (GHM-nsp5, red)) in NMR buffer on a Superdex 75, 10/300 GL (GE Healthcare) column. Horizontal lines indicate fractions of monodisperse nsp5 used for MW determination. (G) A SDS-PAGE showing all purified nsp5 constructs. The arrow indicates nsp5. (H) Exemplary [15N, 1H]-BEST-TROSY spectra measured at 298 K for the dimeric wtnsp5 (upper spectrum) and monomeric GS-nsp5 (lower spectrum). See Supplementary Table SI4 for technical details regarding this figure.