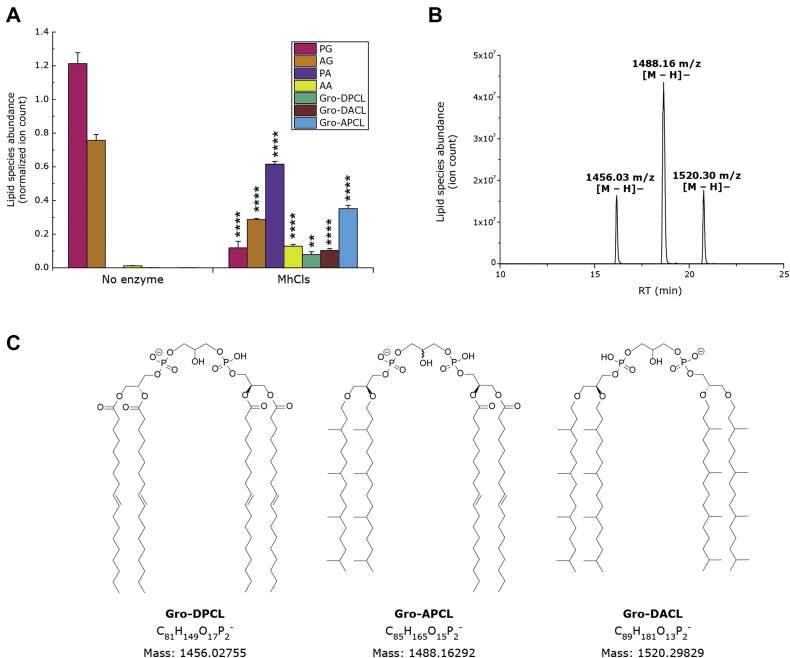
Figure 5.
Synthesis of a bacterial–archaeal hybrid cardiolipin species.A, activity of the archaeal MhCls in the presence of both archaetidylglycerol (AG) and phoshpatidylglycerol (PG). Lipid species PG, AG, phosphatidic acid (PA), archaetidic acid (AA), glycerol-di-phosphatidyl-cardiolipin (Gro-DPCL), glycerol-archaetidyl-phosphatidyl-cardiolipin (Gro-APCL), and glycerol-di-archaetidyl-cardiolipin (Gro-DACL) were analyzed by LC-MS, normalized for the internal standard, and plotted. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance is shown for the enzymatic reaction (MhCls) compared with the control (no enzyme), for each individual lipid species, by using the Student’s t-test analysis; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001. B, LC-MS chromatogram showing the separation of the produced bacterial Gro-DPCL, hybrid Gro-APCL, and archaeal Gro-DACL. C, structures of the three cardiolipin species. Note that in Gro-APCL, the presence of the archaetidyl-group and the phosphatidyl-group makes the central carbon atom of the glycerol head group a chiral center.