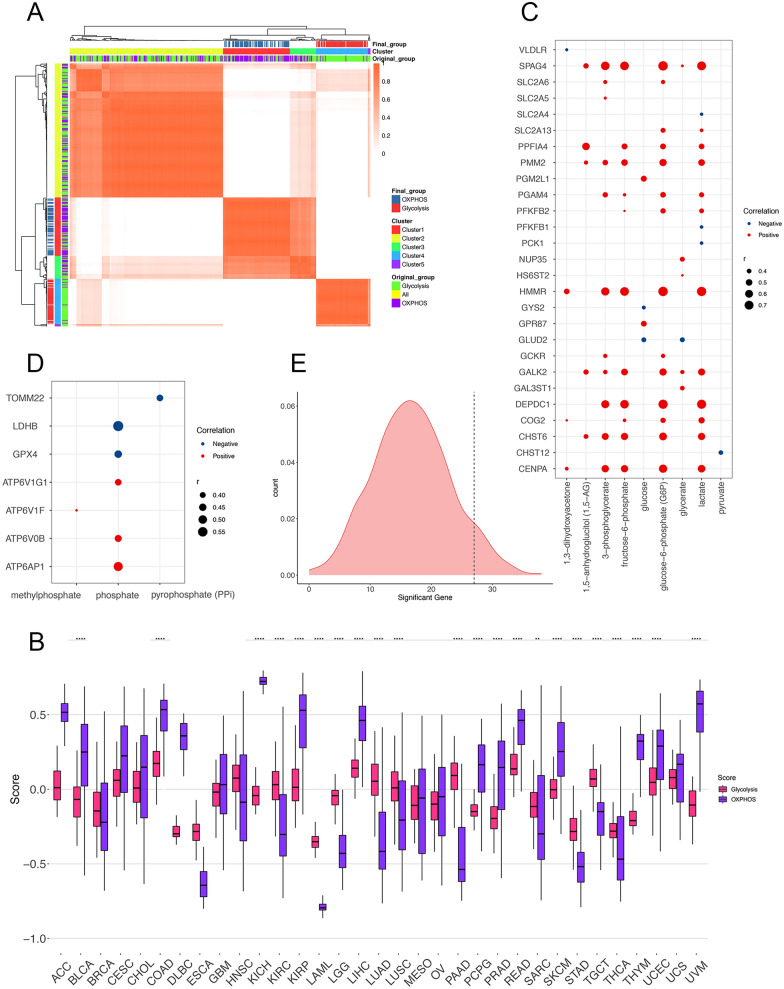
Fig. 1.
A The identification of gene signatures for OXPHOS by consensus clustering algorithm on a pan-cancer scale (k = 5). B The distribution of the Glycolysis score and OXPHOS score across 33 cancer types. Within each group, the scattered dots represent the two scores of each patient. The lines in the boxes represent the median value. The bottom and top of the boxes are the 25th and 75th percentiles (interquartile range). The whiskers encompass 1.5 times the interquartile range. The statistical difference of the two scores was compared through the Wilcoxon test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. C, D The bubble plot shows the correlations between the expression level of signature genes and the abundance of metabolites annotated to Glycolysis (C) and OXPHOS (D) pathways. Significant correlations (Pearson’s correlation, FDR < 0.05) are displayed. Red dots indicate a positive correlation, while blue ones for negative. Dot size is proportional to the strength of the correlation. E The density plot displays the “background distribution” of significant hits when assessing the correlation between the abundance of glycolysis-related metabolites and expression of random-selected gene sets (n = 72 for each gene set, repeated for 1000 times). The black dashed line indicates the true number. FDR, false discovery rates. ACC adrenocortical carcinoma, BLCA bladder urothelial carcinoma, BRCA breast invasive carcinoma, CESC cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma, CHOL cholangiocarcinoma, COAD colon adenocarcinoma, DLBC lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, ESCA esophageal carcinoma, GBM glioblastoma multiforme, HNSC head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, KICH kidney chromophobe, KIRC kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, KIRP kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma, LAML acute myeloid leukemia, LGG brain lower grade glioma, LIHC liver hepatocellular carcinoma, LUAD lung adenocarcinoma, LUSC lung squamous cell carcinoma, MESO mesothelioma, OV ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma, PAAD pancreatic adenocarcinoma, PCPG pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma, PRAD prostate adenocarcinoma, READ rectum adenocarcinoma, SARC sarcoma, SKCM skin cutaneous melanoma, STAD stomach adenocarcinoma, TGCT testicular germ cell tumors, THCA thyroid carcinoma, THYM thymoma, UCEC uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma, UCS uterine carcinosarcoma, UVM uveal melanoma