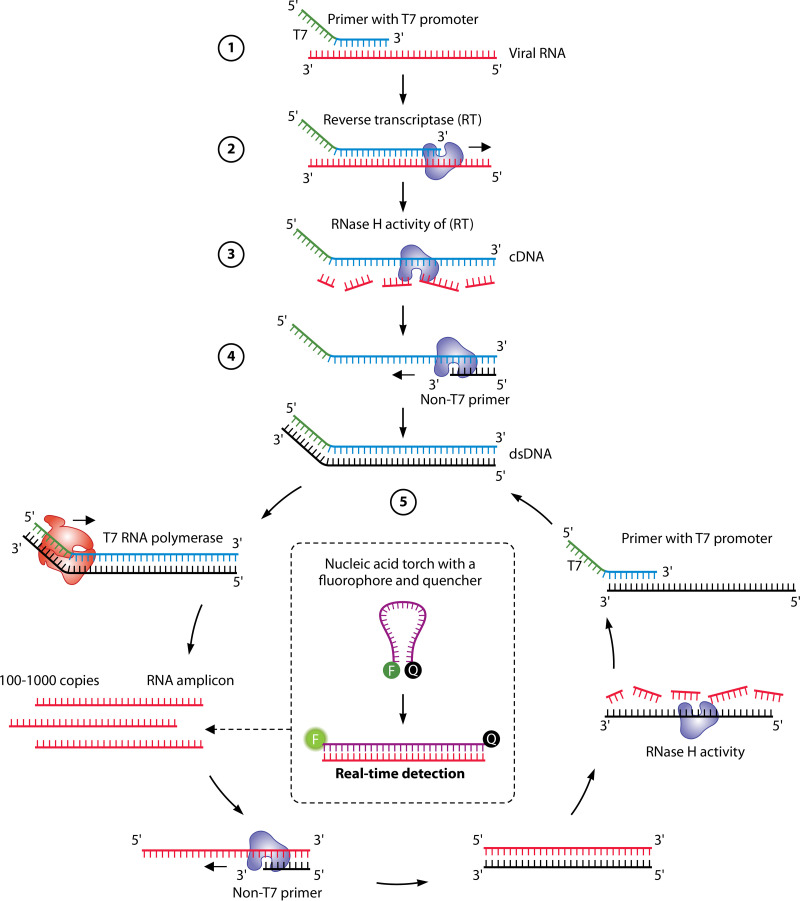
FIG 5.
Principle of TMA. (1) The reactions use a reverse primer that is complementary to the sequence of the RNA template, but the reverse primer also contains an overhang with a promoter sequence for T7 RNA polymerase at its 5′ end. (2) Reverse transcription is conducted by the RT; the newly transcribed cDNA includes both the target sequence and the T7 promoter. (3) The RNA template is digested by the RNase H activity of the RT. (4) dsDNA is produced by the DNA polymerase activity of the RT. (5) The produced dsDNA is used as the template for transcription mediated by the T7 RNA polymerase. RNA is thereby amplified severalfold and, through the activity of the same enzyme(s), can serve as the template for a new TMA reaction. As the cycle progress, exponential amplification ensues. Detection of the amplified RNA is usually accomplished using sequence-specific molecular beacons (“torch”) or hybridization probes targeting the single-stranded RNA (ssRNA).