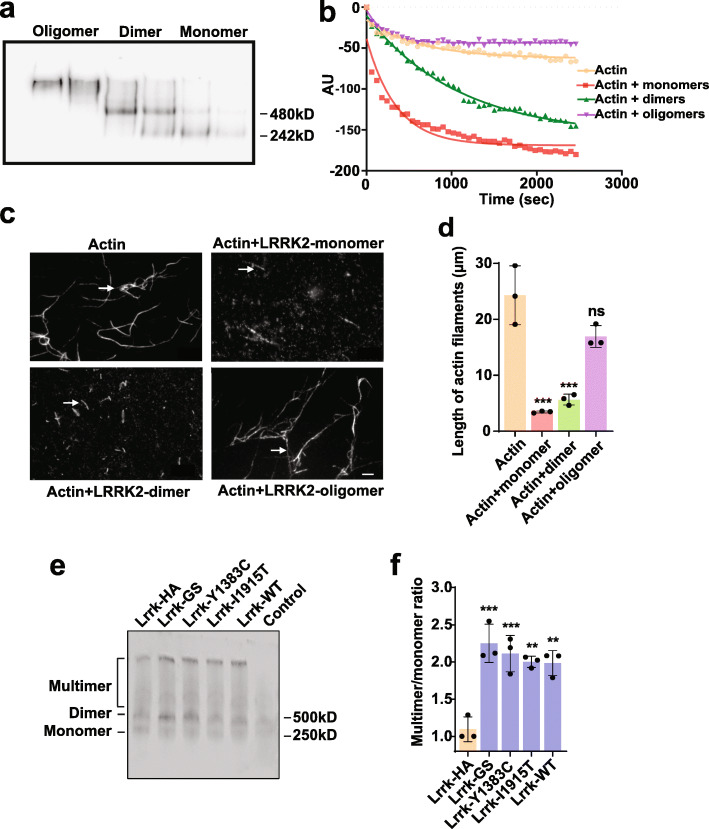
Fig. 3.
Lrrk enhances actin depolymerization by severing F-actin filaments in vitro and in vivo. a, Purified human LRRK2 protein was subjected to size exclusion chromatography following a one hour incubation to allow dimerization and oligomerization. Fractions containing putative monomer, dimer and oligomer pools were collected and confirmed by native gel electrophoresis and western blotting for LRRK2. b, Increased actin depolymerization mediated by monomers and dimers, but not oligomers of LRRK2 in a fluorescence-based pyrene actin depolymerization assay. n=3. c, Severing of fluorescently labeled actin filaments (arrows) by monomers and dimers of LRRK2, but not oligomers, in an in vitro assay, as quantified in (d). n=3. Scale bar in (c) represents 10 µm. e, Native western blotting of fly heads using endogenous Lrrk tagged with HA shows that multimer to monomer ratios in vivo, as quantified in (f) are increased in Lrrk mutants when compared to controls. n=3-6 per genotype. Data are represented as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, ns, not significant, ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test analysis. Control is nSyb-GAL4/+. Lrrk-HA is LrrkHA, nSyb-GAL4/+. Flies are 10 days old