Figure 1.
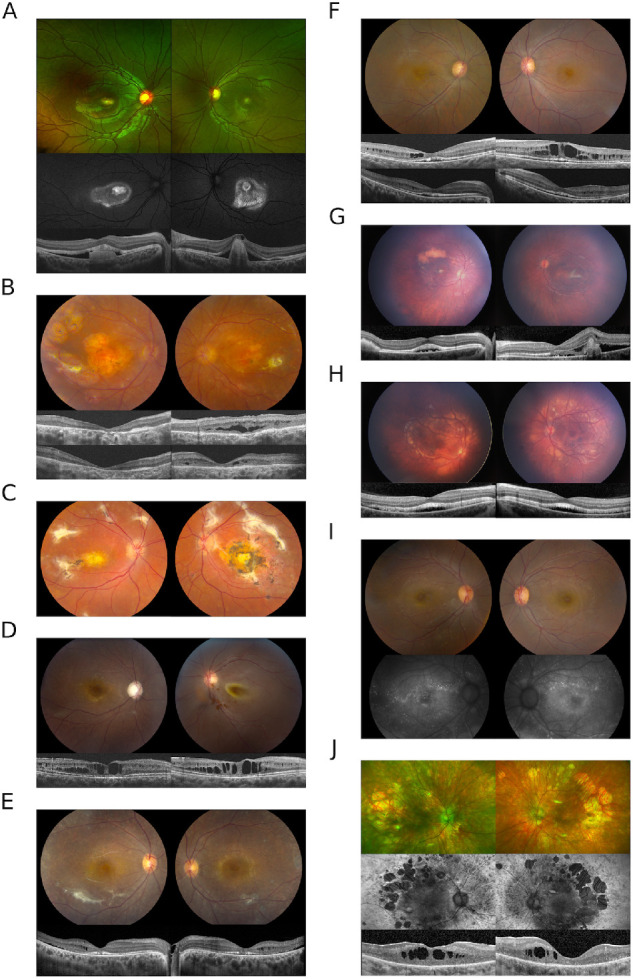
(A) Bilateral subfoveal lesions are present in the proband from family A. OCT imaging reveals subretinal material OD and fibrotic appearing pigment epithelial detachment OS with subretinal lucency separating the neurosensory retina from the RPE OU. Mild pigmentary changes are seen on color imaging and a ring of hyperautofluorescence extends beyond the subfoveal lesion. Punctate lesions (not shown) were observed in the far peripheral retina. (B) Chorioretinal atrophy accompanied by scarring and scattered punctate depositions throughout the peripheral retina in the proband from family B. OCT images at presentation (upper) and after CAI treatment (lower) show a partial resolution of intraretinal fluid in the left eye. (C) The fundus image of the sibling to proband B. (D) Macular cystic changes and optic nerve cupping in the right eye of proband C; retinal detachment in the left eye. The OCT images depict the right eye at two different time points, at presentation (left) and after one year (right). (E) Color fundus images from patient D show diffuse retinal atrophy with white dots and subretinal fibrosis. Intraretinal fluid, SRF, and disruption of the IS/OS juction can be seen on OCT. (F) Cystic macular changes in patient E on fundus images and OCT. The top row of OCT images shows cystic changes at presentation and the lower row corresponds to resolution with CAIs. (G) Fundus photos of proband F show focal yellow deposits in the macula with a superior large yellow conglomerate of subretinal material OD. The left eye has a perifoveal subretinal fibrosis. The disease in both eyes does not extend beyond the vascular arcades. OCT images show subretinal fluid at foveal center in the right eye and the subretinal fibrosis with subretinal fluid on the left eye. (H) Photos show more extensive disease than the sibling in (G) as the yellow deposits extend beyond the vascular arcades including the nasal retina. The corresponding OCTs show a shallow but extensive area of subretinal fluid. (I) Proband G had small scattered hyperfluorescent lesions on FAF. (J) Widespread retinal atrophy with hyperfluorescence in the periphery and patchy mid-peripheral loss of signal with macular hypofluorescence.
