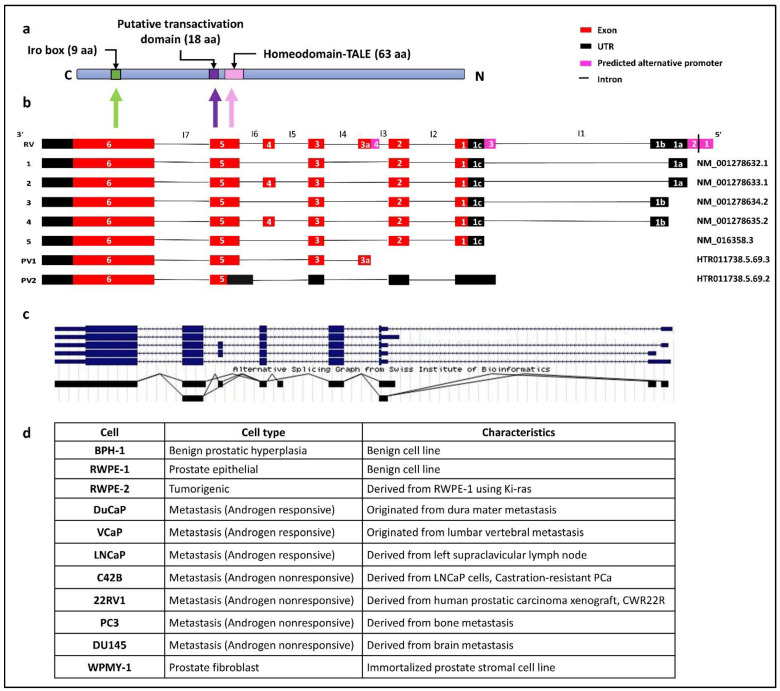
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic representation of IRX4 domains. The predicted localization of the homeodomain, putative transactivation domain, irobox and the number of amino acids (aa) in different domains of the IRX4 proteins. The different domain encoding regions from the IRX4 gene have been shown with the arrows, C-C-terminal, N-N-terminal regions. (b) The predicted IRX4 transcripts according to gene databases. The five known IRX4 transcripts: transcript 1(NM_001278632.1), transcript 2 (NM_001278633.1), transcript 3 (NM_001278634.2), transcript 4 (NM_001278635.2) and transcript 5 (NM_016358.3) and two predicted IRX4 transcripts (PV1: HTR011738.5.69.3 and PV2: HTR011738.5.69.2) according to the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics gene predictions and the novel putative exon (exon 3a) are presented with alignment with the Reference Variant (RV). Introns are labelled from I1 to I7. (c) Alternative splicing graph detailing alternative splicing (AS) events of the IRX4 gene by the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, adapted from the UCSC genome browser. Lines on the plot show the exon–exon junctions. The overlapping lines denote the two types of exon–exon junction, suggestive of the presence of transcripts of IRX4. (d) The characteristics of PCa cell lines used in the study.