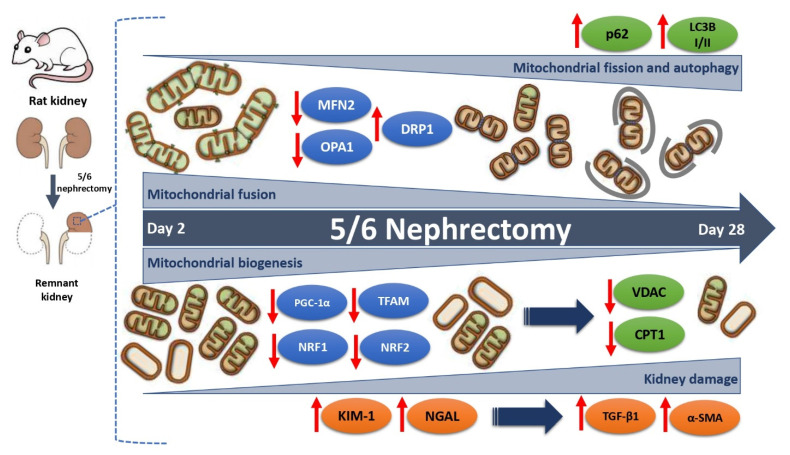
Figure 6.
Evolution of mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics changes in the time interval between day 2 and day 28 after 5/6 nephrectomy (5/6Nx). In this interval, there is a progressive reduction in the levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) and 2 (NRF2), and mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM), which implies the downregulation of the mitochondrial biogenesis machinery over time. This reduction appears from day 2 and is progressive over time, triggering the decrease in mitochondrial proteins such as voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) from day 2 to day 28. There is a positive correlation between the reduction in mitochondrial biogenesis factors and the increase in the tubular damage proteins kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and the fibrotic markers transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β1) and alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). In addition, a slow and gradual change in mitochondrial dynamics from fusion to fission is also shown. This trend started with a reduction on day 2 after 5/6Nx in the fusion proteins mitofusin 2 (MFN2) and optic atrophy 1 (OPA1), favoring the mitochondrial fragmentation observed from 7 days, and continued with an increase in dynamin-1-like protein (DRP1) 28 days after surgery. In addition, macroautophagy markers ubiquitin-binding protein p62 and microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B I and II (LC3B-I/II) progressively increased with the time, implying the induction of autophagy. This mechanism would principally be present at a chronic stage.