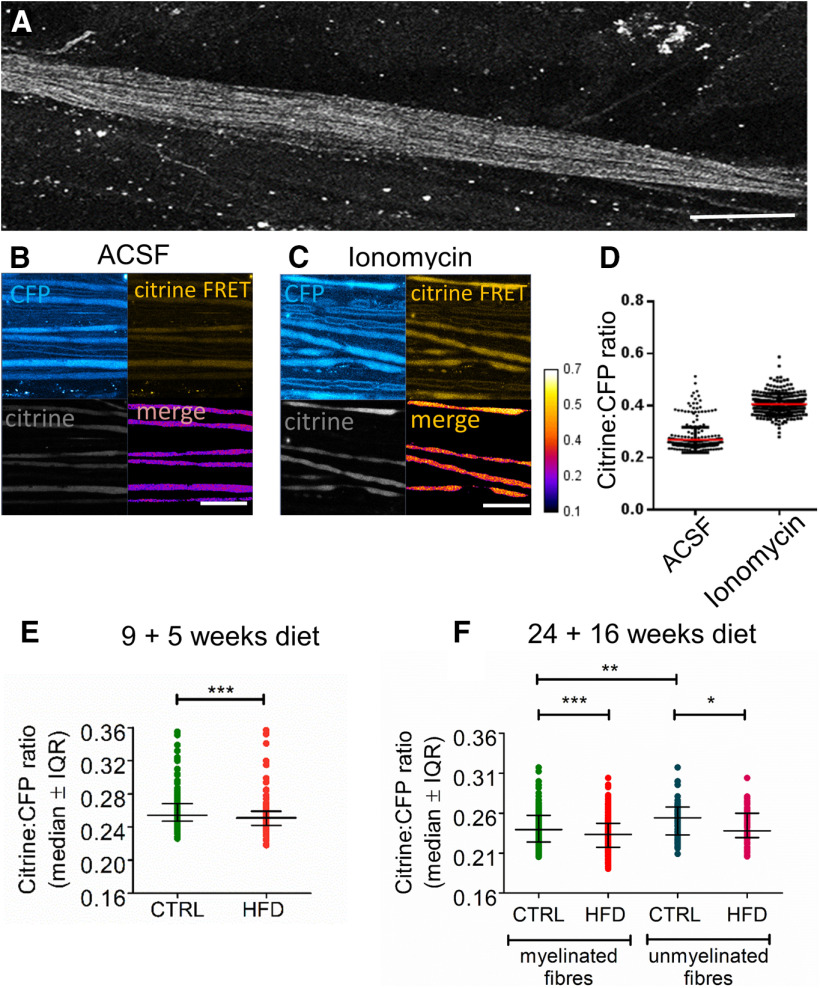
Figure 7.
HFD mice exhibit reduced [Ca2+]i levels in saphenous nerve axons in vivo. A, Confocal image of an exposed saphenous nerve in vivo in a Tn-XXL mouse. Scale bar, 400 μm. B, C, High-magnification confocal image in CFP, citrine, and citrine FRET channels with a merge of CFP and citrine FRET, of saphenous nerve axons bathed in vivo with aCSF (B) or ionomycin (100 μm) for 20 min (C). Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Citrine to CFP intensity ratio increases after incubating control Tn-XXL mouse saphenous nerve axons in ionomycin (100 μm) for 20 min (n = 4 mice per group, n = 257-318 axons per group). E, Pilot data of HFD 9 + 5 mice exhibit reduced [Ca2+]i in myelinated axons compared with controls. *p < 0.05 (Mann–Whitney test). Data are mean ± SEM. n = 4 control mice with n = 318 axons; n = 4 HFD mice with n = 148 axons. F, HFD 24 + 16 mice exhibit reduced [Ca2+]i in both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers compared with controls. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; Kruskal–Wallis test. Data are mean ± SEM. n = 9 control mice with n = 70 axons; n = 10 HFD mice with n = 60 axons. Weight gain and impaired glucose tolerance in Tn-XXL (calcium reporter) mice are shown in Extended Data Figure 7-1.