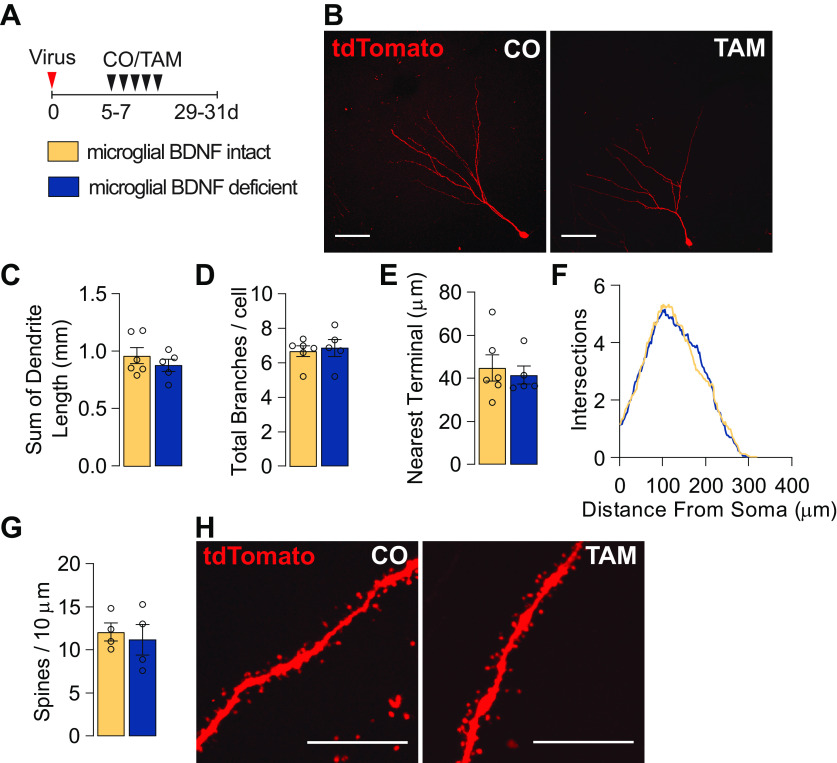
Figure 4.
Microglial BDNF deficiency does not influence the dendritic morphology of adult-born hippocampal neurons. A, Experimental timeline for tdTomato retrovirus intrahippocampal injection into Cx3cr1creERT2 x Bdnf flox/flox mice followed by either tamoxifen or corn oil gavage. B, Confocal images of dendritic morphology of tdTomato-positive retrovirus-labeled adult-born hippocampal neurons. Scale bar, 50 μm. C, D, Quantification of the total length of dendrites (t(9) = 0.92, n = 5–6; C) and the number of branches (t(9) = 0.34, n = 5–6; D). E, Quantification of the mean distance to the nearest neighboring dendritic terminal (t(9) = 0.43, n = 5–6). F, Sholl analysis of the complexity of dendrites (F(1,9) = 0.44, n = 5–6). G, Quantification of the density of dendritic spines (t(6) = 0.43, n = 4). H, Representative images of dendritic spines. Scale bar, 10 μm. Data represent the mean ± SEM. Statistical tests: Student's t test, C–E, G; repeated-measures two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc comparison test, F. Small circles represent individual mice.