Figure 5.
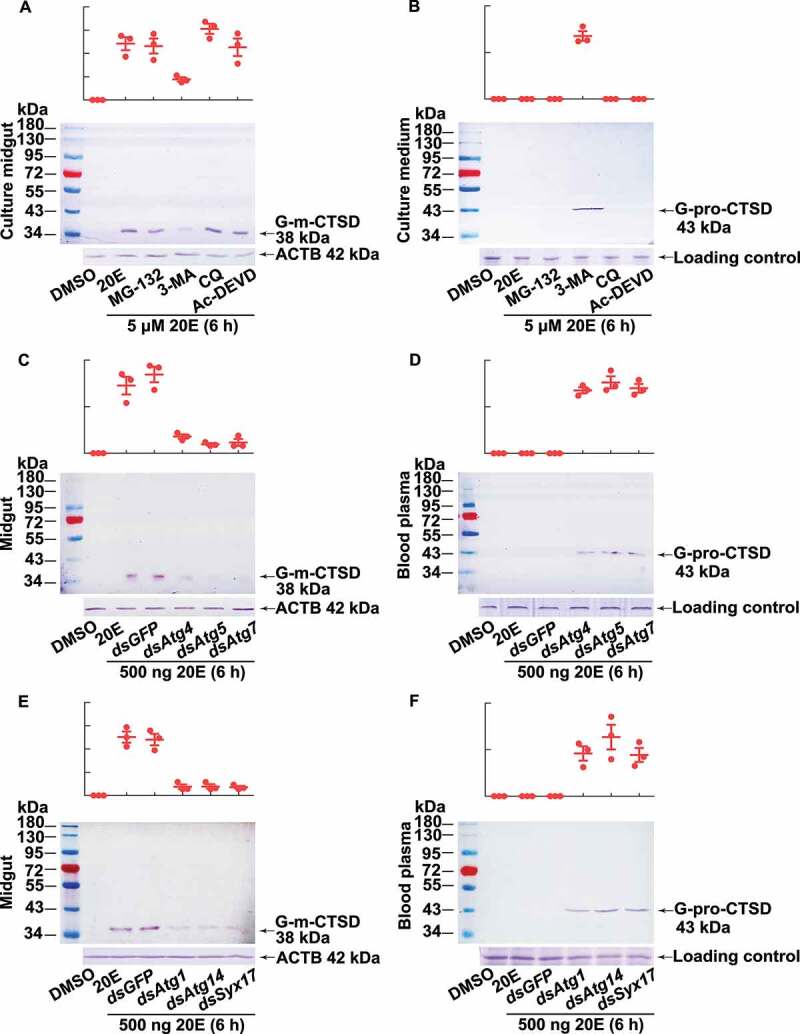
Western blotting showing that CTSD maturation relied on autophagy. (A) G-m-CTSD in the midgut after treatment with different inhibitors. The isolated midgut was cultured in Grace’s medium with MG-132 (2 µM, final concentration), 3-MA (10 µM), CQ (25 µM), and Ac-DEVD/Ac-DEVD-CHO (10 µM) for 1 h, followed by 20E incubation (5 µM for 6 h). DMSO was the solvent control for 20E. (B) The secreted G-pro-CTSD in the culture medium after the treatment as (A). ACTB was detected as protein quality control. Grace’s medium was used for tissue culture medium loading control by SDS-PAGE. (C) G-m-CTSD in the midgut after Atg4, Atg5, and Atg7 knockdown (2 μg dsRNA were injected to sixth instar 6 h larva twice in 48 h), followed by 20E incubation (500 ng for 6 h). dsGFP (2 μg twice in 48 h) was the negative control. (D) The secreted G-pro-CTSD in the blood plasma after Atg4, Atg5, and Atg7 knockdown. (E) G-m-CTSD in the midgut after Atg1, Atg14, and Syx17 knockdown (2 μg dsRNA were injected to sixth instar 6 h larva twice in 48 h), followed by 20E incubation (500 ng for 6 h). dsGFP (2 μg twice in 48 h) was the negative control. (F) The secreted G-pro-CTSD in the blood plasma after Atg1, Atg14, and Syx17 knockdown. ACTB was detected as the protein quality control. The loading controls were the proteins of hemolymph by SDS-PAGE as the control for blood plasma. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and statistical analysis was conducted using ANOVA; different lowercase letters indicated significant differences (p < 0.05). The bars indicate the mean ± SD. ImageJ software was used to transform the image data
