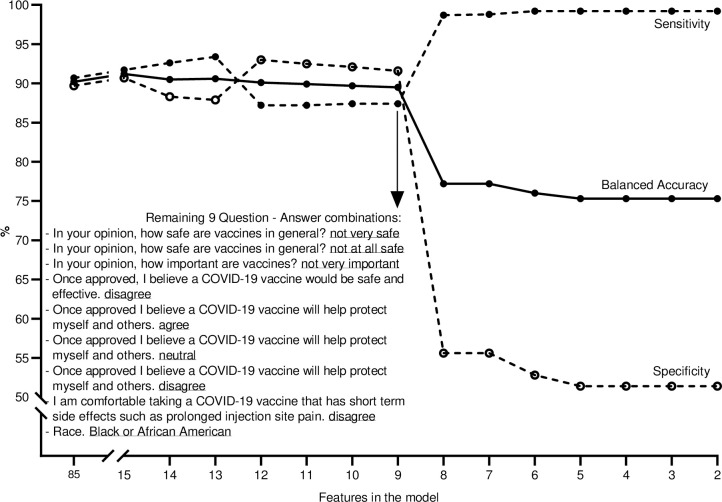
Fig 3. Result of recursive feature elimination algorithms.
Random Forest classification algorithm was constructed to identify a set of determinants able to separate those who are not willing to vaccinate from those who are. The model started with a list of 85 features and predicted the willingness of subjects in the hold-out dataset with 90.2% balanced accuracy (solid line), which is an average of 90.7% sensitivity (dashed line closed circles) and 89.7% specificity (dashed line open circles). The balanced accuracy remained near constant when testing the recursively reduced models, up to the model with 9 remaining features (i.e. 5 questions with a total of 9 answers, see inserted table). This final model showed an 89.5% balanced accuracy with 87.4% sensitivity and 91.6% specificity. Further reduction, removing the least important feature from the set of 9 (i.e. ‘Neutral’ to ‘Once approved, I believe a COVID-19 vaccine will help protect myself and others’), resulted in a 12.3 percent point reduction in balanced accuracy primarily due to misclassification of the not willing to vaccinate (Specificity = 55.6%).