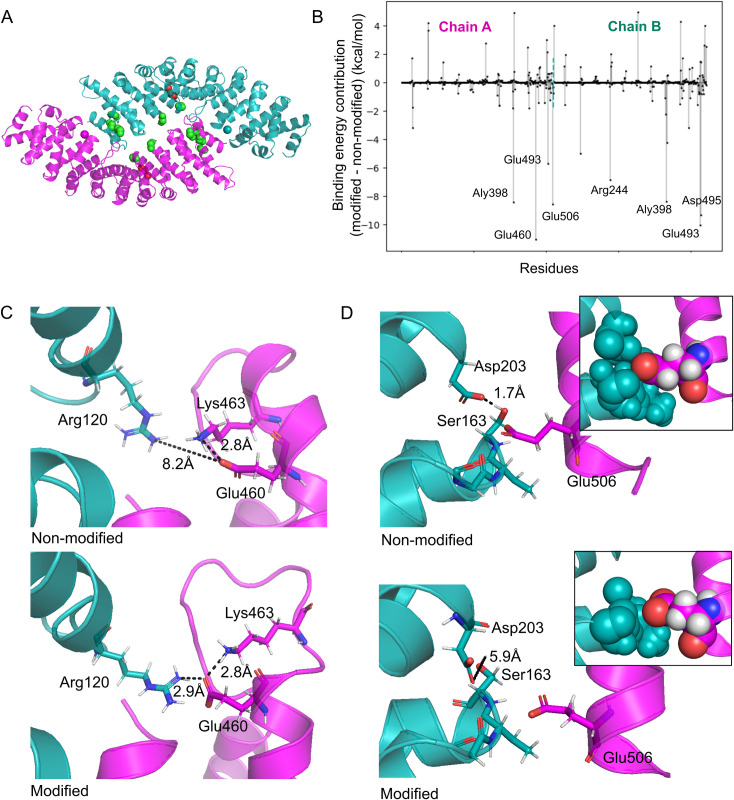
Fig 6. A case study–importin alpha.
A. The initial structure of the Kapα homodimer (PDB ID: 1BK5), with chain A shown in magenta and chain B in cyan. Green space-filling representation is used to denote the backbone atoms of lysine acetylation sites, while red is used for serine phosphorylation sites detected in normal conditions. B. Per-residue decomposition of the Kapα free energy of binding (ΔΔGbind,contribution). Amino acids of homodimer are shown on the x-axis, where the two chains are separated by a dashed cyan line. For each residue, the difference of binding contribution between modified and non-modified complex is shown as a vertical line ending with a dot, where negative values denote residues with a more stabilizing contribution in the modified than in the non-modified complex, and vice versa for the positive. Residues with contributions larger than 5 kcal/mol are labeled. C. Glu460 in chain A is interface located only in the modified complex, and therefore has a large stabilizing ΔΔGbind,contribution, mainly due to interactions with Arg120 from chain B. D. Glu506 has a significantly less destabilizing contribution to binding in the modified complex, where chain B is more distant. The inserted frames depict Glu506 and residues of chain B which are within 5 Å from it in a space-filling representation.