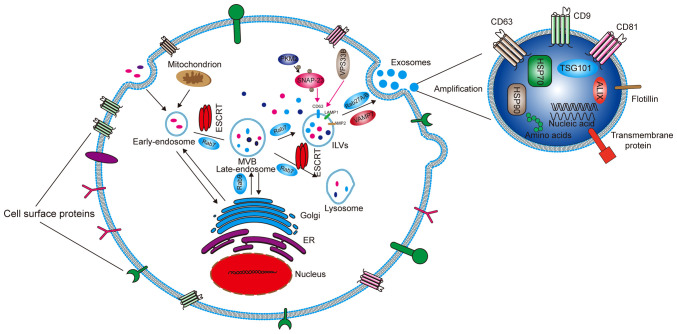
Figure 1.
Formation and secretion mechanism of exosomes and the main components of exosomes. Early endosomes are formed through endocytosis, and then as a result of ESCRT, become late endosomes and then MVBs. After screening, some MVBs become ILVs and some are digested by lysosomes. ILVs are broken down to form exosomes and then released outside the cell. The whole process requires the action of Rab (an ATP protein) to provide ATP. The exosomes mainly contain HSP70, HSP90, TSG101, ALIX, amino acids and nucleic acids. The membrane surface mainly contains transmembrane proteins such as CD9, CD63, CD81 and Flotilin. ESCRT, endosomal sorting complexes required for transport; MVB, multivesicular body; ILV, intraluminal vesicle; Rab, rabphilin; HSP, heat shock protein; TSG101, tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein; ALIX, apoptosis-linked gene 2 interacting protein X; CD, cluster of differentiation; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; VAMP, vesicle-associated membrane protein; LAMP, recombinant lysosomal associated membrane protein; SNAP-23, synaptosomal-associated protein 23; VSP33B, vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 33B; PKM2, pyruvate kinase M2.