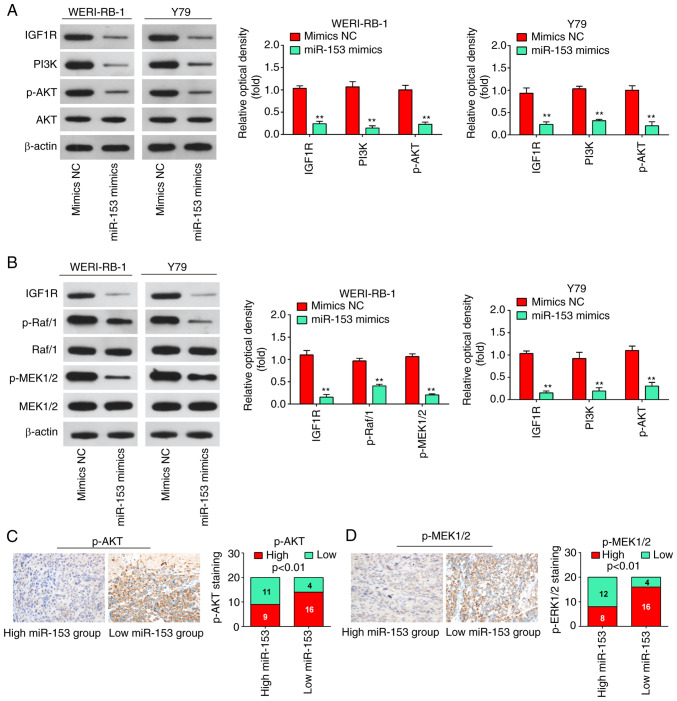
Figure 7.
miR-153 deactivates the PI3K/AKT and Raf/MEK pathway in WERI-RB-1 and Y79 cells by decreasing IGF1R expression. (A) Following transfection, western blot analysis was performed to measure IGF1R, PI3K, p-Akt and Akt expression. The bands were semi-quantitatively analyzed by using ImageJ software, normalized to β-actin density. **P<0.01 vs. mimics NC group. (B) Following transfection, western blot analysis was performed to measure IGF1R, Raf/1, p-Raf/1, p-MEK1/2, and MEK1/2 expression. The bands were semi-quantitatively analyzed by using ImageJ software, normalized to β-actin density. **P<0.01 vs. mimics NC group. (C) Immunohistochemistry was conducted to detect p-AKT in RB tissues with high or low miR-153 expression. Bar graphs demonstrated a significant inverse association between miR-153 and p-AKT expression in RB tissues (n=50). Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three individual experiments. (D) Immunohistochemistry was conducted to detect p-MEK1/2 in RB tissues with high or low miR-153 expression. Bar graphs demonstrated a significant inverse association between miR-153 and p-MEK1/2 expression in RB tissues (n=50). Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three individual experiments. RB, retinoblastoma; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; MEK, mitogen activated protein kinase kinase; miR, microRNA; p, phosphorylated.