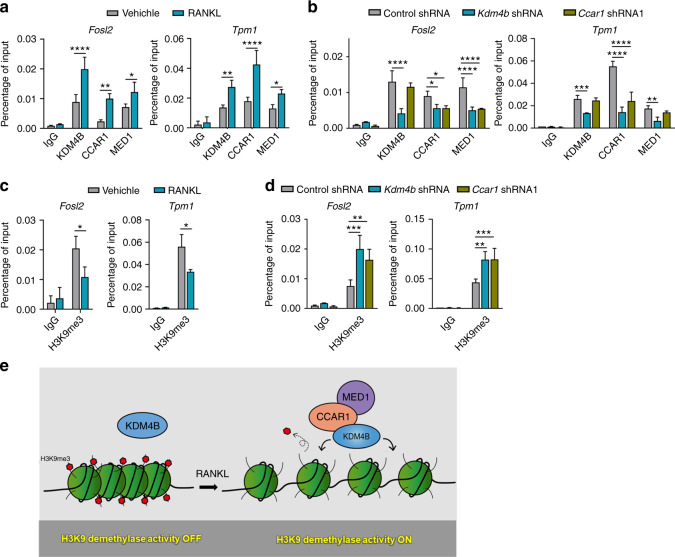
Fig. 5.
KDM4B-dependent recruitment of CCAR1 and MED1. a ChIP-qPCR of KDM4B, CCAR1, and MED1 enrichment upon RANKL treatment (100 ng·mL−1, 30 min) at the Fosl2 (−1.1 kb) and Tpm1 (−0.6 kb) promoters. b ChIP assays of KDM4B, CCAR1, and MED1 localization at target genes in cells depleted of KDM4B or CCAR1 upon RANKL signaling (100 ng·mL−1, 30 min). c ChIP-qPCR of H3K9me3 in the Fosl2 and Tpm1 promoters in the cells evaluated in (a). d ChIP assays of H3K9me3 status in the cells evaluated in (b) upon RANKL signaling. e Schematic representation of the cooperative function of KDM4B, CCAR1, and MED1 in regulating H3K9 demethylation. The data are presented as the mean ± SD values of three independent experiments [two-way ANOVA in (a–d)]. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. See also Supplementary Fig. 5