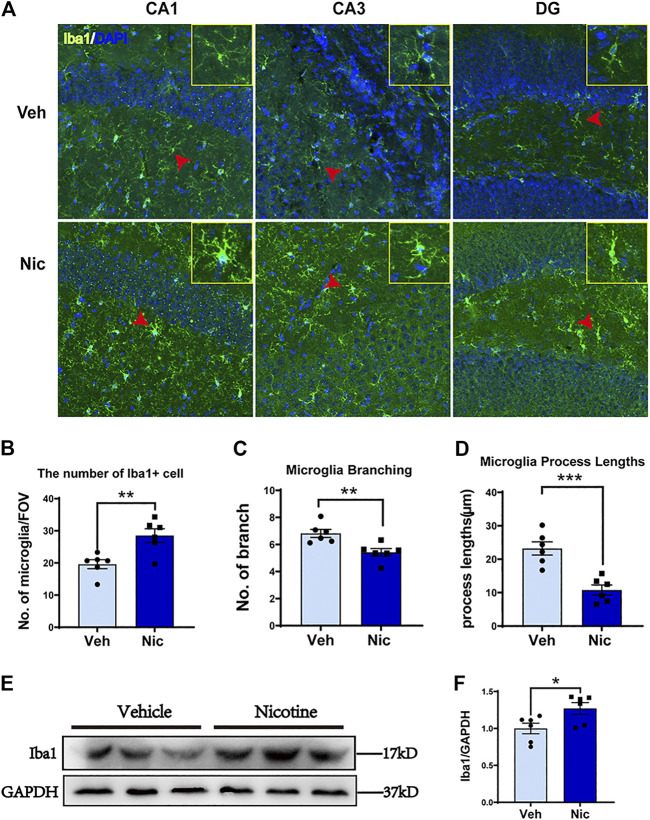
FIGURE 5.
Nicotine exposure increased the number of Iba1 positive microglial cells and promoted M2-like microglial polarization in the nicotine-exposed offspring’s hippocampus. The morphology of microglia was detected by immunofluorescence staining. Representative images of the Iba1 expression in CA1, CA3, and DG were shown (A). Olympus FV3000 Confocal Microscopy was used to get a Z-stack for 3-D reconstruction, and images showed that microglia cells changed their morphology from branching (in the control) to amoebic (in the nicotine-exposed group) in the offspring hippocampus. Nicotine exposure increased hippocampus microglial number (B), but decreased microglial branching (C) and microglial process lengths (D). CA1, CA3, and DG areas were used to generate the date presented in B-D. A point represented a calculated average of each measurement. (E, F) Iba1 protein level was increased in nicotine offspring revealed by western blot, as compared to vehicle offspring. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. Scale bar = 50 μm all data are means ± SEM.