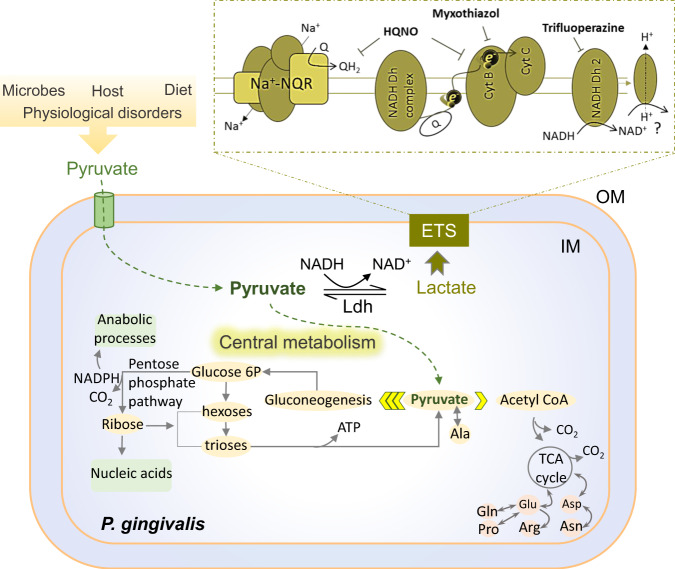
Fig. 7. Proposed model of possible bioenergetics system and metabolism of the monocarboxylates pyruvate and lactate in P. gingivalis that are deduced from the effectiveness of applied uncouplers in RF assay and metabolomic analysis.
Pyruvate availability in the intracellular and extracellular milieu of host cells is impacted by various external factors. P. gingivalis efficiently transports exogenous pyruvate inside to couple with the metabolism of serum components toward the enhancement of the PPP intermediates that are required for biosynthetic processes, resulting in the increase of cell proliferation and biomass in the biofilm community. ETS electron transport system, Ldh lactate dehydrogenase, Cyt cytochrome, NADH Dh NADH dehydrogenase, Na+–NQR the sodium pumping NADH quinone oxidoreductase, Q quinone, e electron, NAD nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADPH nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, Glucose 6P glucose-6-phosphate, Glu glutamic acid, Asp aspartic acid, Gln glutamine, Pro proline, Arg arginine, Asn asparagine, Ala alanine, ATP adenosine triphosphate; HQNO 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline N-oxide, IM inner membrane, OM outer membrane.