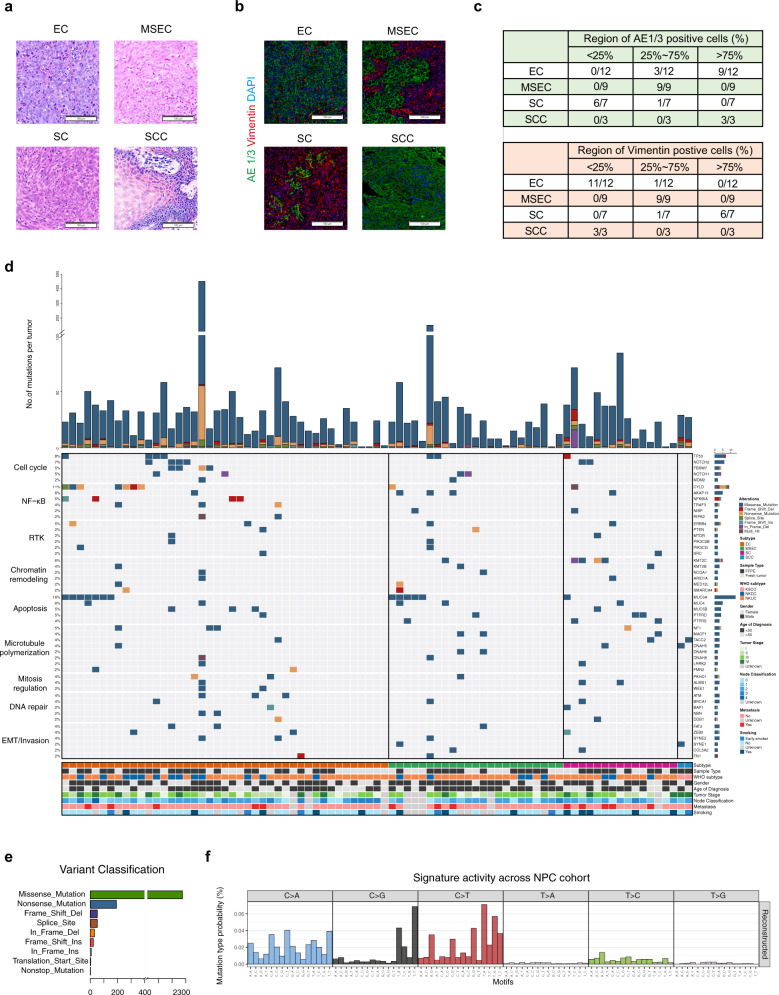
Fig. 1. Histological and molecular landscape of NPC subtypes.
a Representative histological view of four NPC subtypes. The EC subtype is characterized by round epithelial tumor cells, while the SC subtype is characterized by spindle sarcomatoid tumor cells. The MSEC subtype encompasses both round epithelial and spindle sarcomatoid tumor cells. SCC is a minor subtype of NPC characterized by a keratinizing phenotype. Scale bar, 100 μm. The H&E staining images are representatives of 106 tumors consist of 57 EC subtype, 20 SC subtype, 26 MSEC subtype, and 3 SCC subtype tumors. b Immunohistochemical staining of NPC markers. The EC subtype is positive for the epithelial cell marker AE1/3 and negative for the sarcomatoid cell marker vimentin, whereas the SC subtype is positive for the sarcomatoid cell marker vimentin and negative to epithelial cell marker AE1/3. The MSEC subtype exhibited mixed pattern of both epithelial and sarcomatoid cell markers. Scale bar, 100 μm. The immunohistochemical images are representatives of 31 tumors consist of 12 EC subtype, 9 MSEC subtype, 7 SC subtype, and 3 SCC subtype tumors. c Summary table of NPC marker expression levels among subtypes. The top panel shows levels of AE1/3 positive cells in EC (n = 12), MSEC (n = 9), SC (n = 7), and SCC (n = 3) tumors. The bottom panel presents levels of vimentin-positive cells in EC (n = 12), MSEC (n = 9), SC (n = 7), and SCC (n = 3) tumors. The corresponding immunohistochemical images are demonstrated in Fig. 1b and Supplementary Fig. 1a. d Top recurrent protein coding SNVs identified from this cohort and represented in pathway wise, including cell cycle, NF-κB signaling, receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), chromatin remodeling, apoptosis, microtubule polymerization, mitosis regulation, DNA repair and EMT/invasion. SNV mutational rate for each tumor is shown at the top of the panel. Information of subtype, sample type, WHO subtype, gender, age of diagnosis, tumor stage, node classification, metastasis and smoking status are shown at the bottom. Only paired tumor samples (n = 88) were assigned for SNV identification. e Detailed somatic variation types and amounts discovered from this NPC cohort. A total of 2662 somatic mutations included 2306 missense mutations, 191 nonsense mutations, 47 splice site, 51 frame shift deletion, 31 in frame deletion, 23 frame shift insertion, 8 in frame insertion, and 5 others (n = 88 tumors). f Overall mutational signature of this NPC cohort revealed C > A and C > T base substitutions are predominant mutational signature in NPC (n = 88 tumors).