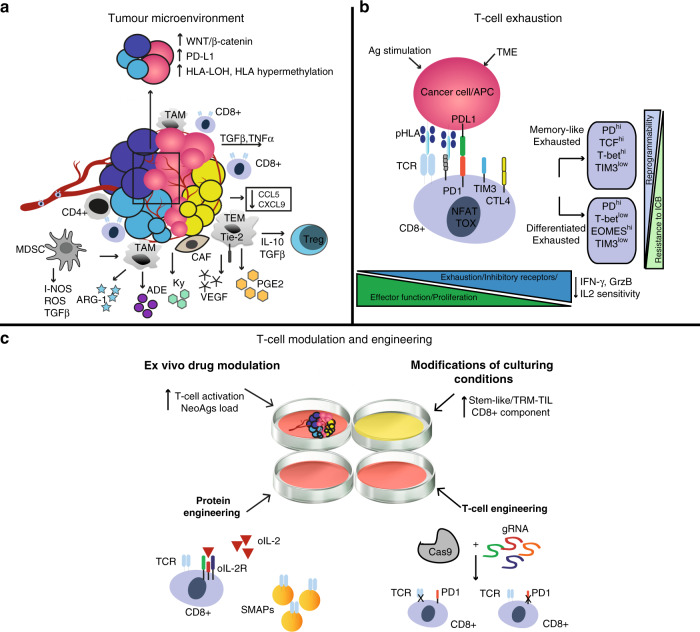
Fig. 2. T cell conditioning to overcome the immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment.
a Immuno-evasion mechanisms in the tumour microenvironment. A representative example of an ‘excluded’ (cold) T-cell tumour is shown. Some of the most studied immune cells along with their ligand–receptor and secreted growth factors (chemokines and cytokines) known to promote immunoevasion are shown. In the black box, examples are given of cancer genetic alterations linked to an immuno-evasive tumour microenvironment (ADE adenosine, ARG1 Arginase 1, CAFs cancer-associated fibroblasts, DC dendritic cell, IL interleukin, iNOS inducible nitric oxide synthase, KYN: kynurenine, MDSC myeloid-derived suppressor cells, NO nitric oxide, PGE2 prostaglandin E2, ROS reactive oxygen species TAMs tumour-associated macrophages, TGF-β transforming growth factor-β, Treg regulatory T cell, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor). In the black box are highlighted genetic mechanisms linked to a cold TME. b T cell exhaustion in solid tumours. A representative image of transitions from an effector (Teff) to an exhausted (Tex) T cell is shown. Chronic antigen exposure and the TME pressure promote the activity of transcription factors (such as NFAT, TOX), which increases the expression of exhaustion-associated molecules such as PD1, LAG3, and TIM3, and the downregulation of effector cytokines such as IFNγ, GrzB and IL-2 sensitivity. GrzB Granzyme B, IL2 interleukin-2, TME tumour microenvironment, TRM tissue-resident memory. c Potential interventions to increase TIL efficacy during the expansion of T cells for ACT. The tumour microenvironment (TME) can be modulated ex vivo with different drugs (such as epigenetics, immunometabolic drugs) or interleukins (e.g. IL-2, IL-15) to boost the growth and activation of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes, to increase the number of neoantigens (epigenetic drugs) or to preferentially expand TIL-specific subtypes such as tissue resident memory T cells (TRM-TILs). CRISPR–Cas9 ribonuclear protein complexes loaded with single-guide RNAs can be electroporated into TILs or normal T cells for gene editing. Shown here is an example of deletion of TCRs (off-the-shelf T cells) and of inhibiting immune checkpoint receptors such as programmed death 1 (PD-1) in T cells. Protein engineering can be used for the creation of orthogonal IL-2–IL-2 receptor pairs, which consist of a mutant orthogonal IL-2 cytokine (oIL-2) and mutant IL-2 receptor (oIL-2R) that interact specifically with each other but do not interact with their wild-type counterparts. SMAPs (supramolecular attack particles) can be produced in vitro and grafted to relevant specific TCRs for adoptive transfer.