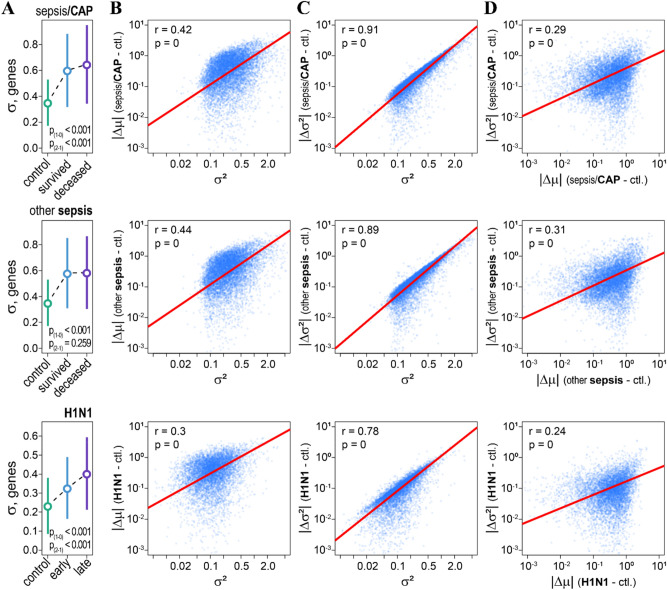
Figure 1.
H1N1 and sepsis coordinately affect mean gene expression and inter-individual gene expression variability. (A) Inter-individual variability in whole blood gene expression (σ) increases in sepsis/CAP (top), other sepsis (mid), and H1N1 (bottom) patients as compared to healthy individuals. p(1–0)—p-values of t-tests comparing differences in inter-individual gene expression variability of healthy individuals (control) with survived (sepsis) and early H1N1 infected patients. p(2–1)—p-values of t-tests comparing differences of survived (sepsis) and early H1N1 infected patients with deceased (sepsis) and late H1N1 infected patients. Circles and whiskers indicate means and standard deviations respectively. (B) Correlations between variances in whole blood gene expression (σ2) and absolute changes in mean gene expression (|Δμ|) for healthy individuals (ctl.) and patients (sepsis, H1N1). Due to the fluctuation-response relationship, the magnitude of the mean gene expression response depends on its variance. We estimated common variances for genes in healthy and sepsis/CAP patients (top), healthy and other sepsis patients (mid), and healthy and H1N1 patients (bottom). (C) Correlations between variances in whole blood gene expression (σ2) and absolute changes in inter-individual gene expression variability (|Δσ2|) for control individuals (ctl.) and patients (sepsis, H1N1). (D) Correlations between absolute changes in mean gene expression (|Δμ|) and in inter-individual gene expression variability (|Δσ2|).