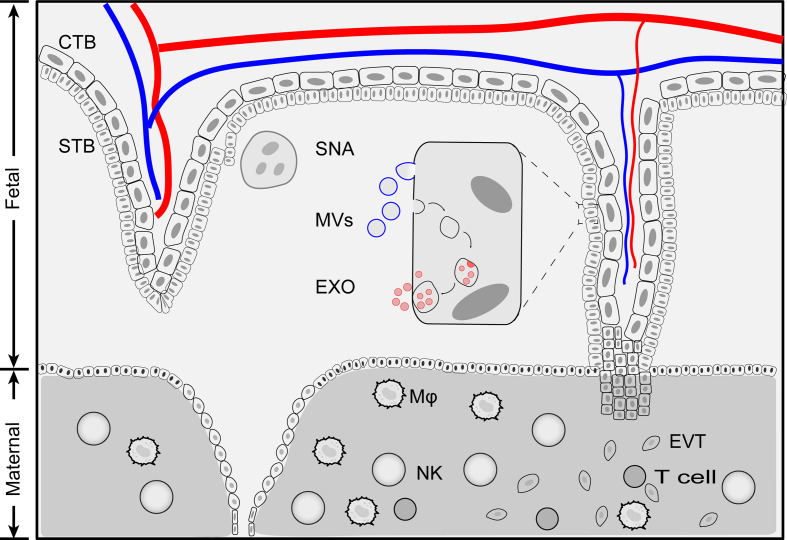
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of placenta extracellular vesicles. Placenta derived extracellular vesicles can be divided into four categories: exosomes, microvesicles, apoptotic bodies and syncytial nuclear aggregates based on size and biogenesis pathway. Exosomes are generated by multivesiculuar body (MVB)-intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) system. first MVBs are generated by plasma membrane inward budding. Further, invagination of the late endosomes forms intraluminal vesicles (exosomes) within multivesiculuar body (MVB). Exosomes release to extracellular space when MVB fuse with membrane plasma. During this processes, membrane components and cytosolic materials are loaded into exosomes. Microvesicles and apoptotic bodies are produced by outward budding of plasma membrane and the size range of 200 nm - 5 μm. Syncytial nuclear aggregates (SNA) are clusters of syncntiotrophoblast with multiple nuclei per SNA. CTB, cytotrophoblast; Exo, exosomes; EVT, extravillous trophoblast; MVs, microvesicles; Mφ, macrophage; NK, Natural killer cells; STB, syncytiotrophoblast; SNA, syncytial nuclear aggregates.