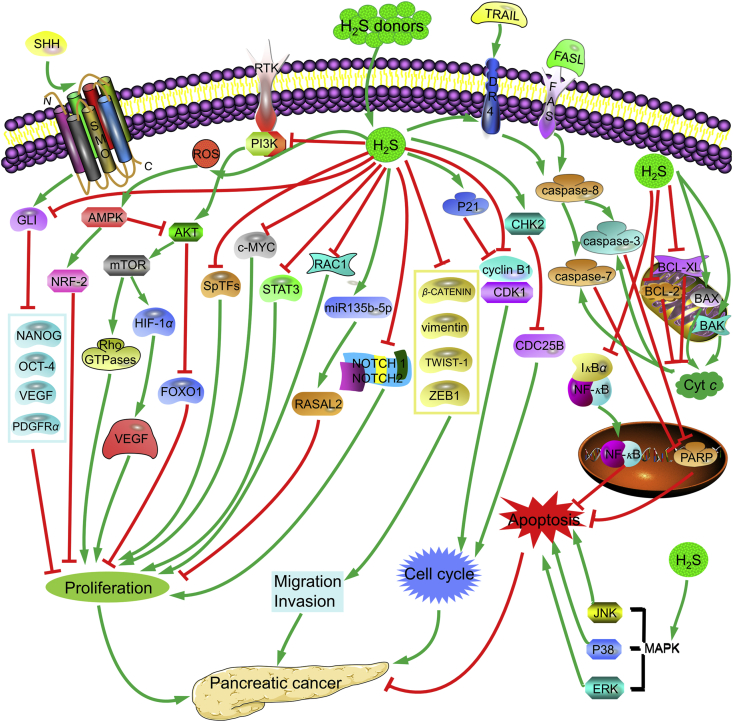
Figure 3.
Possible signaling pathways of ITCs and DATS involved in the antiproliferation of pancreatic cancer. ITCs, including ERU, SFN, BITC and PEITC, belong to natural H2S donors. They slowly release H2S in biological environments69, 70, 71. The relatively high concentrations of ITCs and DATS exhibit antiproliferative effects on pancreatic cancer by inducing apoptosis, arresting cell cycle and suppressing invasion and migration of tumor cells72,73. In brief, these donors suppressed cell proliferation by inhibiting SHH86, PI3K/AKT/mTOR92, SPTFs94, STAT394, RAC190, and NOTCH95, and activating AMPK79 and RASAL282 signaling pathways. Moreover, they also inhibited early metastasis by down-regulating ZEB186, β-CATENIN85, TWIST-185, and vimentin85. Further, they arrested cell cycle by up-regulating P2188, activating CHK288, and down-regulating cyclin B1/CDK1102 and CDC25B87. In addition, they induced apoptosis through activating caspase-374, caspase-774, BAK95, BAX102, P3875, JNK75, DR477 and ERK76, and inhibiting BCL-285, BCL-XL95, NF-κB110 and PARP78.