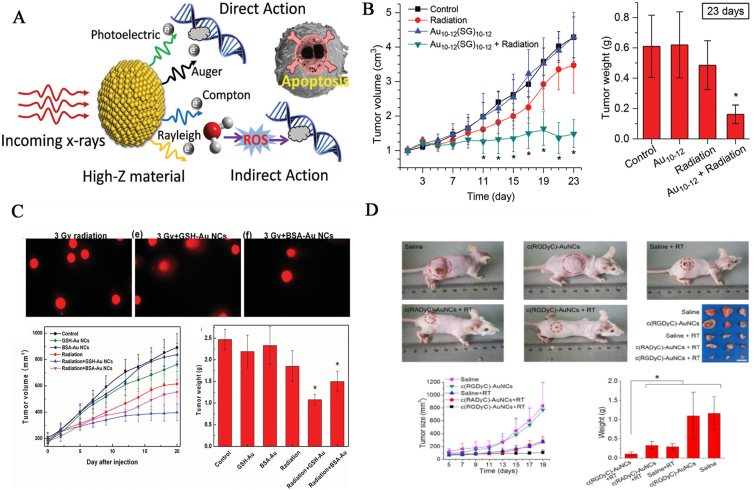
Figure 4.
(A) Schematic illustration of interactions of X-rays with high-Z materials and the corresponding direct and indirect effects on cancer cells. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 140. Copyright © 2017, the Royal Society of Chemistry. (B) Schematic illustration of the structure of Au10(SG)10 nanomolecule for high radiotherapy. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 143. Copyright © 2014, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (C) Schematic illustration of the structures of GSH-Au25 NCs and BSA-Au25 NCs nanomolecules for high radiotherapy. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 145. Copyright © 2014, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (D) Schematic representation of c(RGDyC)-Au NCs, which exhibited selectively enhanced targeting and accumulation of αvβ3 integrin-positive cancer cells with red/NIR fluorescence emission. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 146. Copyright © 2017, Elsevier.