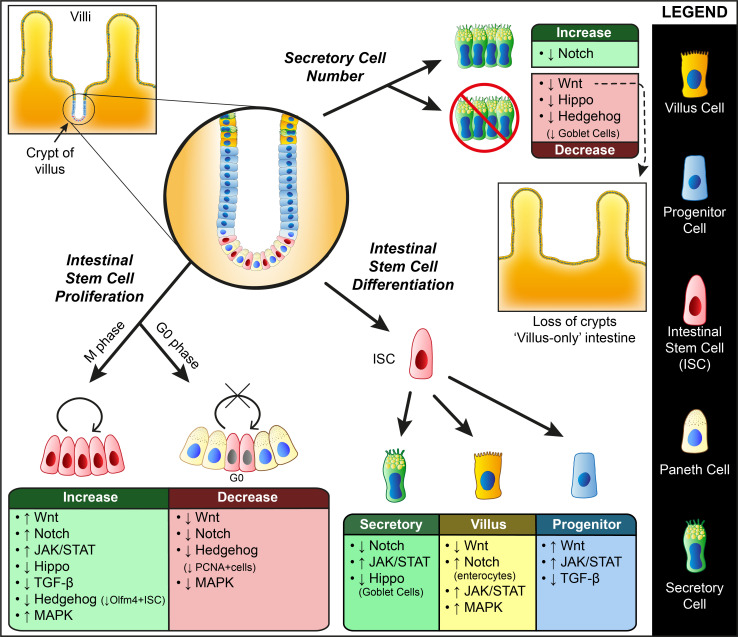
Figure 1.
Genetic regulation of ISC (intestinal stem cell) dynamics. ISCs maintain all the differentiated cell types in the intestinal epithelium. The figure shows a magnified crypt morphology with a distribution of different cell types along the crypt and various signaling pathways modulating ISC dynamics. The direction of arrows near the pathways indicates upregulation or downregulation. In general, Wnt, Notch, JAK/STAT, and MAPK pathways are promoters of proliferation in ISCs, whereas TGF-β and Hippo are negative regulators. Loss of Wnt and hedgehog leads to differentiation defects with loss of crypt proliferation and loss of ISCs, although there is contradicting evidence where hedgehog increases proliferation. The notch is also necessary to maintain ISCs in their progenitor phenotype as loss of Notch was found to induce differentiation. JAK/STAT also plays a role in cell fate specification as loss of signaling causes defective differentiation and failure in specification.