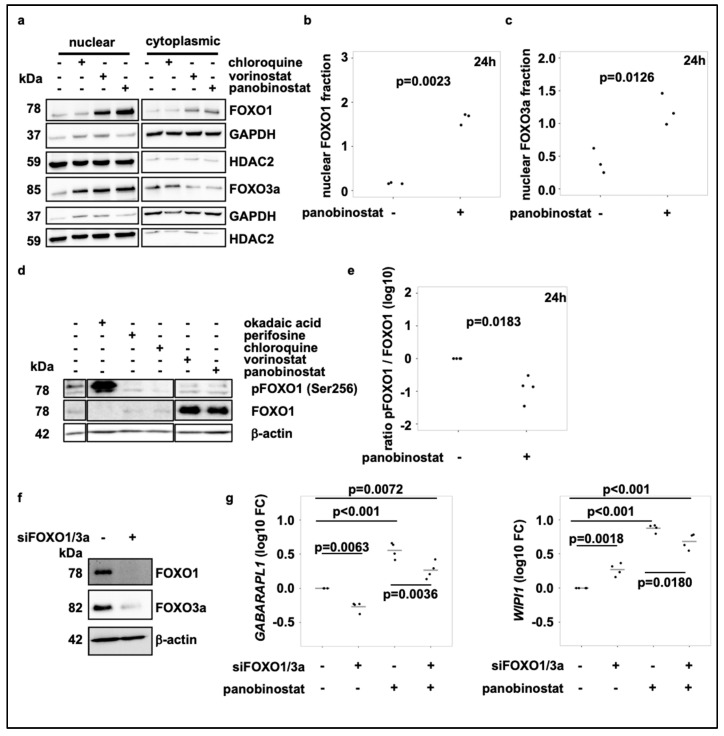
Figure 4.
Broad-spectrum HDAC inhibitor treatment activates FOXO1 via the PI3K-AKT-pathway and induces FOXO nuclear translocation. (a) Representative subcellular localization analysis of FOXO1 and FOXO3a in SK-N-BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cells treated for 24 h with chloroquine (50 µM), vorinostat (500 nM) or panobinostat (10 nM) for 24 h. GAPDH was used as cytoplasmic marker, HDAC2 served as nuclear marker. (b,c) Quantification of FOXO1 (b) and FOXO3a (c) nuclear protein of at least three individual Western blots analogous to figure (a). (d) Western blot analysis of pFOXO1 and FOXO expression after treatment of SK-N-BE(2)-C cells with chloroquine (50 µM), vorinostat (500 nM) or panobinostat (10 nM) for 24 h. Okadaic acid (1 µM) and perifosine (5 µM) were used as positive and negative control, respectively. All samples were applied to the same gel and blotted on one membrane. Treatments with inhibitors/substances not relevant for the figure were cut from the analysis. (e) Quantification of the pFOXO1 to FOXO1 ratio from Western blot analysis from four individual experiments, normalized to solvent control. Statistical analyses: t-test. (f) Western blot analysis of FOXO1 and FOXO3a in SK-N-BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cells 5 days after transfection with control or FOXO1 and FOXO3a siRNA (pool of three different siRNAs for each target; pool of 6 siRNAs in total), respectively. (g) Realtime RT-PCR analysis of GABARAPL1 and WIPI1 after transfection of SK-N-BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cells with control or FOXO1 and FOXO3a siRNA (pool of 3 siRNAs for each target; pool of 6 siRNAs in total). Cells were additionally treated for the last 24h with either panobinostat or a solvent control. Statistical analyses: ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.