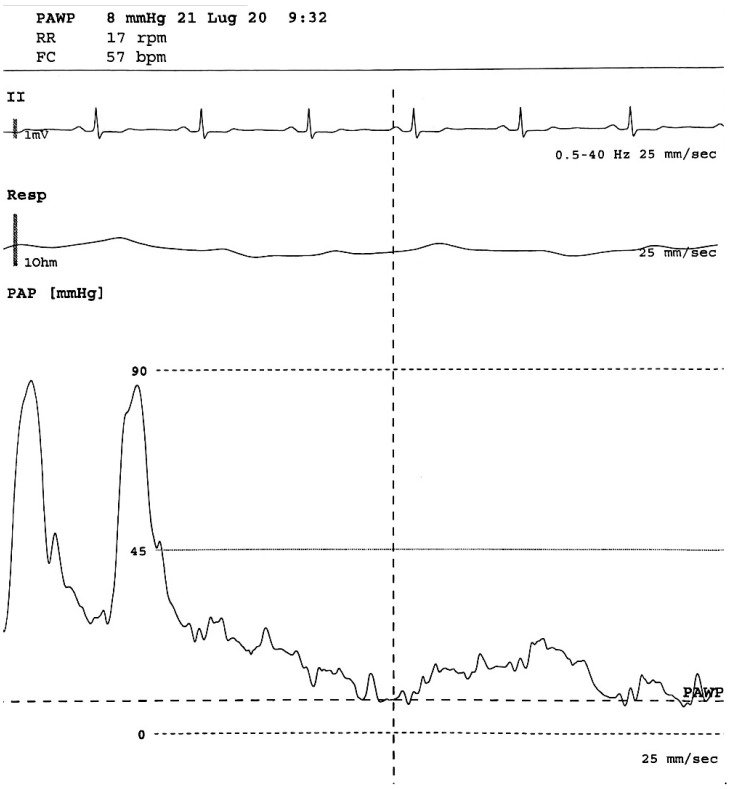
Figure 2.
From below: pulmonary arterial pressure, respiratory and EKG waveforms during arterial catheterization. The first part of the pressure trace reflects the pressure in a pulmonary artery (large swings, dicrotic notch), then the balloon is inflated and the tip of the Swan Ganz catheter floats until it wedges in a small artery (small swings synchronous with respiratory rate), allowing a pulmonary arterial wedge pressure (PAWP) to be obtained, which is an indirect measure of left ventricle pressure.