Figure 1.
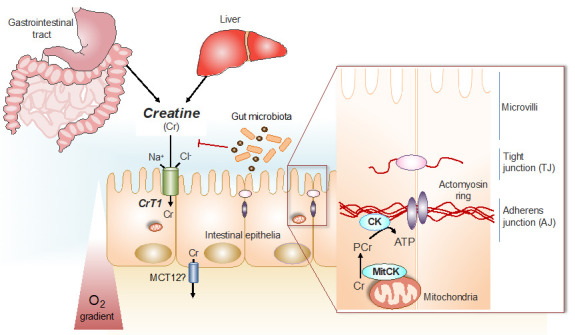
Cr/CK shuttle and the intestinal mucosal barrier. Cr is derived from dietary sources in the gastrointestinal tract, or by de novo synthesis primarily in the kidney and in the liver [12]. The Na+ and Cl− dependent creatine transporter (CrT1), expressed in the apical membrane of intestinal epithelial cells, facilitates Cr uptake from the gut lumen [11,14]. Potential routes for Cr absorption into systemic circulation include paracellular movement by solvent drag transport, or via basolateral Cr transport by the monocarboxylate transporter 12 (MCT12) [15]. Gut microbiota express specific enzymes that can mediate Cr and creatinine (Crn) breakdown. In hypoxic intestinal epithelial cells, cytosolic CK localizes to apical adherens junctions in complex with the actomyosin cytoskeletal network, providing a conduit for rapid ATP generation during the energy-dependent processes of epithelial junction assembly and barrier restitution [16]. Adapted from [17].
