Figure 3.
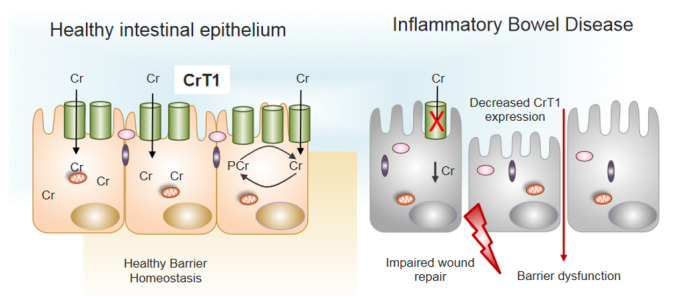
Decreased expression of CrT1 in IBD promotes barrier dysfunction. Normal expression of CrT1 on the apical surface of intestinal epithelia (left panel) results in adequate supplies of Cr via dietary sources to promote healthy barrier function and intestinal homeostasis. Patients with IBD express lower levels of CrT1 (right panel) and disrupt the Cr-PCr energy shuttle to the extent that wound healing potential and barrier are dysfunctional (see [14,16] for further details).
