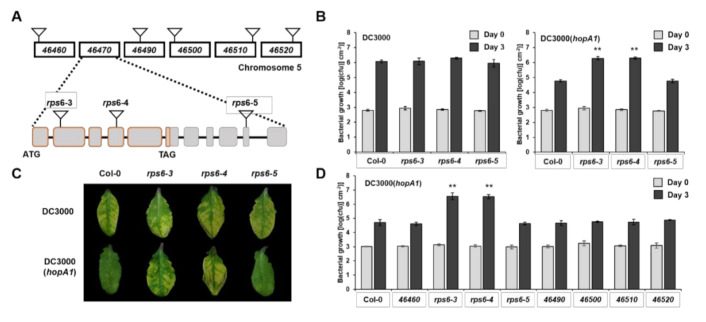
Figure 1.
RPS6 (At5g46470) recognizes HopA1Pss61 in Arabidopsis Col-0 accession. (A) Schematic diagram of chromosome 5 around RPS6 (At5g46470) and position of T-DNA insertion along the genes. rps6-3 and rps6-4 possess T-DNA insertion in exon 2 and exon 4, respectively, while rps6-5 in exon 10; (B) In planta bacterial growth was measured in Col-0, rps6-3, rps6-4, and rps6-5 on day 0 (gray columns) and day 3 (black columns) after inoculation with DC3000 (left) and DC3000(hopA1Pss61) (right); (C) Plants were inoculated with a bacterial suspension at a density of 5 × 106 cfu/mL suspensions of DC3000 (top) and DC3000(hopA1Pss61) (bottom). Photos were taken 4 days post-inoculation; (D) In planta bacterial growth was measured in Col-0, At5g46460, At5g46490, At5g46500, At5g46510, At5g46520, rps6-3, rps6-4, and rps6-5 on day 0 (gray columns) and day 3 (black columns) after inoculation with DC3000(hopA1Pss61); (B,D) Plants were inoculated with a bacterial suspension at a density of 2 × 105 cfu/mL. Values represent averages of cfu/cm2 leaf tissue from quadruplicate samples, and error bars denote standard deviation. Asterisks indicate that the growth of DC3000(hopA1Pss61) on day 3 was significantly different between Col-0 and rps6-3 or rps6-4, as determined by a two-tailed Student’s t-test (** p < 0.01). This experiment was repeated twice with similar results.