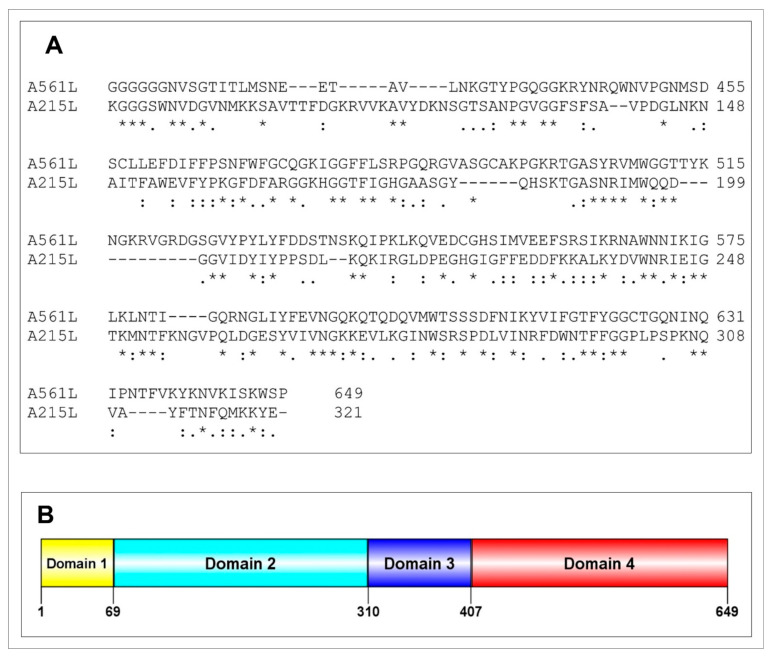
Figure 1.
A561L protein characteristics: domains and possible functions: (A) Amino acid sequence pairwise alignment of a carboxyl-terminal domain of CDS A561L with the carboxyl terminus of CDS A215L; A215L was previously characterized as a polysaccharide lyase [vAL-1 protein] [38]. (B) Predicted domains in A561L—domain 4 is the part of the protein that resembles A215L (domains were identified using InterPro domain prediction database [39] with manual curation). Domain 1 has a transmembrane domain and the closest match is a transporter protein encoded by Listeria kieliensis although the E-value was low, 3.6 × 10−1; Domain 2 has the best hit to a TolA protein of Trichomonas vaginalis (Tol proteins are involved in the stability of the outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria) with an E-value of 4.1 × 10−14 but it also resembles a peptidase S8 domain-containing protein from Tetradesmus obliquus with an E-value of 9.3 × 10−8; Domain 3 resembles a LEA 2 domain-containing protein (late embryogenesis abundant protein, which plays a role in abiotic stress response and tolerance in plants and are part of the hypersensitive response to plant pathogen infection) encoded by Selaginella moellendorffii with an E-value of 6.9 × 10−6; and Domain 4 resembles an alkaline alginate lyase/1–4 polyglucuronic acid lyase/polysaccharide lyase family 14 with an E-value of 2.1 × 10−14.