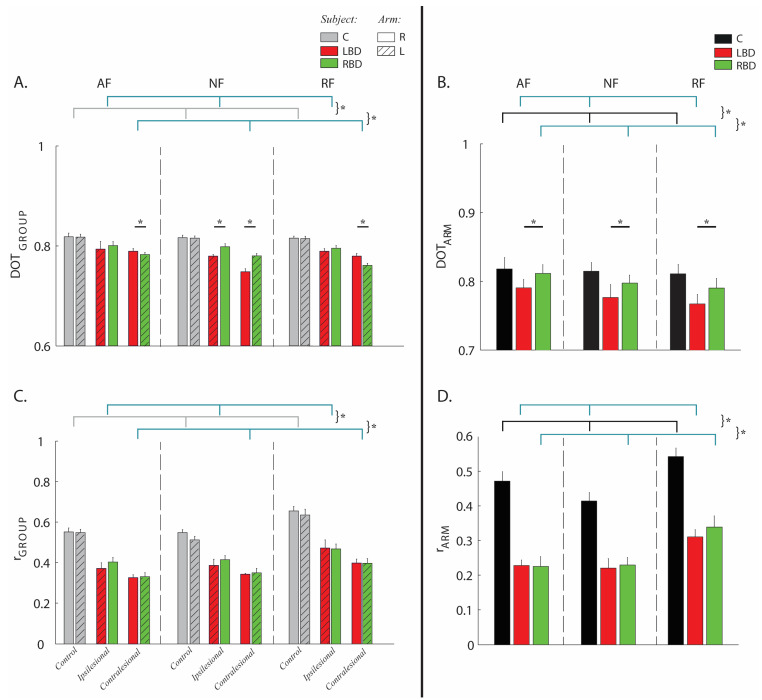
Figure 6.
Comparison of weight and activation coefficients of the muscle synergies. RBD group had weight coefficients less altered than the LBD group in both arms and more similar between the two sides of the body. The force fields reduced the differences in muscle activities between arms and among populations. Panels (A,B): comparison of weight coefficients by the scalar product (DOT). Panels (C,D): comparison of activation coefficients by Pearson correlation (r). Left column: stroke subjects (LBD, red bars; RBD, green bars) compared to matched controls (C, grey bars), i.e., inter-groups indicator for the right (bars with uniform color) and left (bars with diagonal lines) arm in presence of assistive (AF), resistive (RF) and in absence of external force (NF) compared to the same indicator computed intra-group (grey bars) in the controls. Right column: comparison between the two arms of the same subject (C, black bar), left (LBD, red bar) and right (RBD, green bar) brain damaged in presence of assistive (AF), resistive (RF) and in absence of external force (NF). The error bars indicate the standard error. * indicates significant differences (p < 0.05).