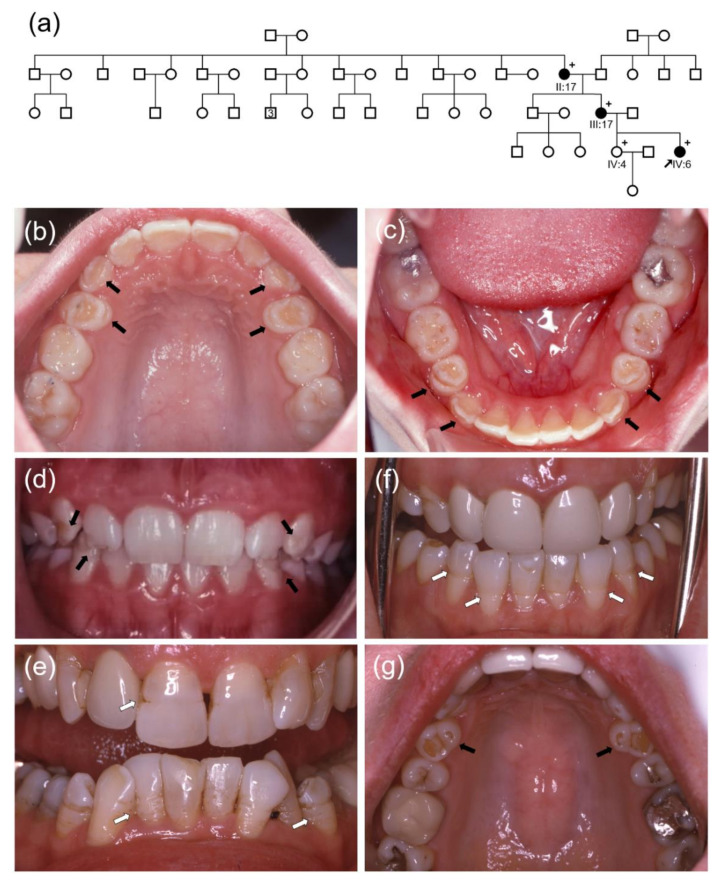
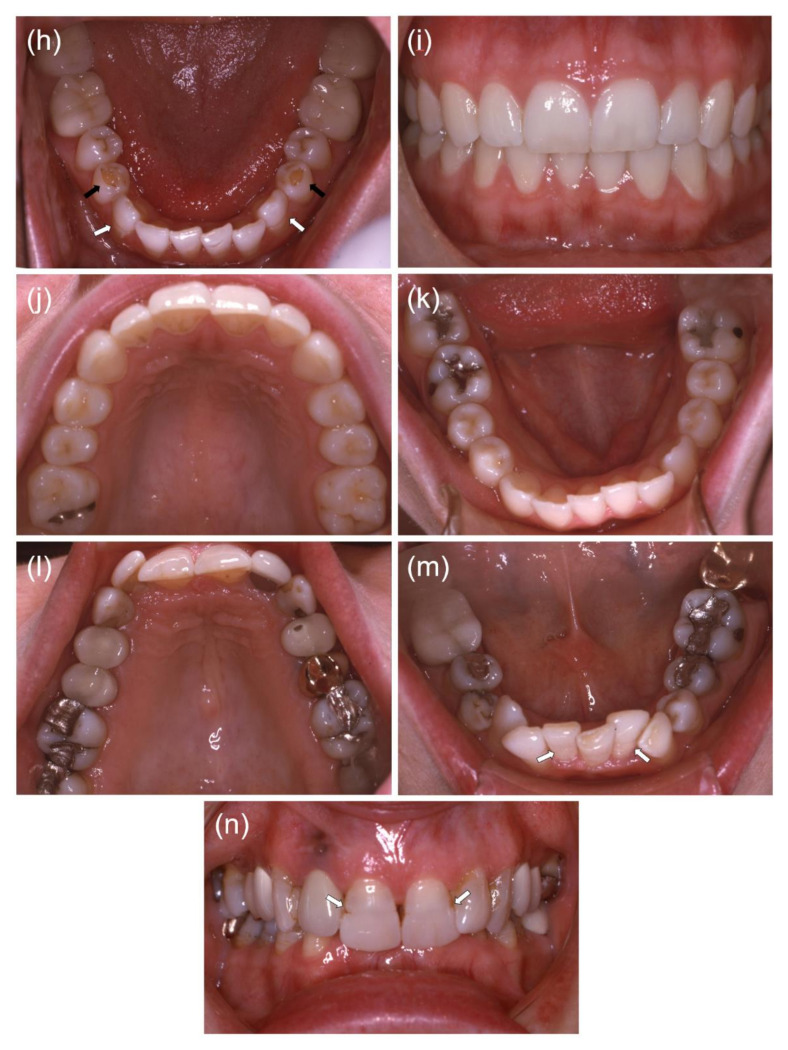
Figure 1.
(a) Pedigree of the study family. The black arrow denotes the proband. The plus sign (+) indicates participating individuals in this study. The number in the symbol indicates the number of siblings. (b–d) Clinical photos of the proband (IV:6). Black arrows indicate hypoplastic enamel defects. The maxillary central incisors look normal, and the mandibular incisors do not show horizontal hypoplastic defects. (e) Frontal clinical photo of the grandmother of the proband (II:17). White arrows indicate hypoplastic horizontal grooves. (f,g) Clinical photos of the mother of the proband (III:17). White arrows indicate hypoplastic horizontal grooves. Her maxillary anterior teeth were treated with porcelain full crown prosthetics. Hypoplastic defects in the maxillary first premolars are indicated with black arrows. (h) Clinical photos of the mother of the proband (III:17). Hypoplastic defects (black arrows) are shown in the mandibular first premolars, and horizontal hypoplastic grooves (white arrows) are shown in the anterior teeth. (i–k) Clinical photos of the sister of the proband (IV:4). Her dentition looks normal, without any noticeable hypoplastic enamel defects. (l–n) Clinical photos of the grandmother of the proband (II:17). White arrows indicate hypoplastic horizontal grooves in the anterior teeth.