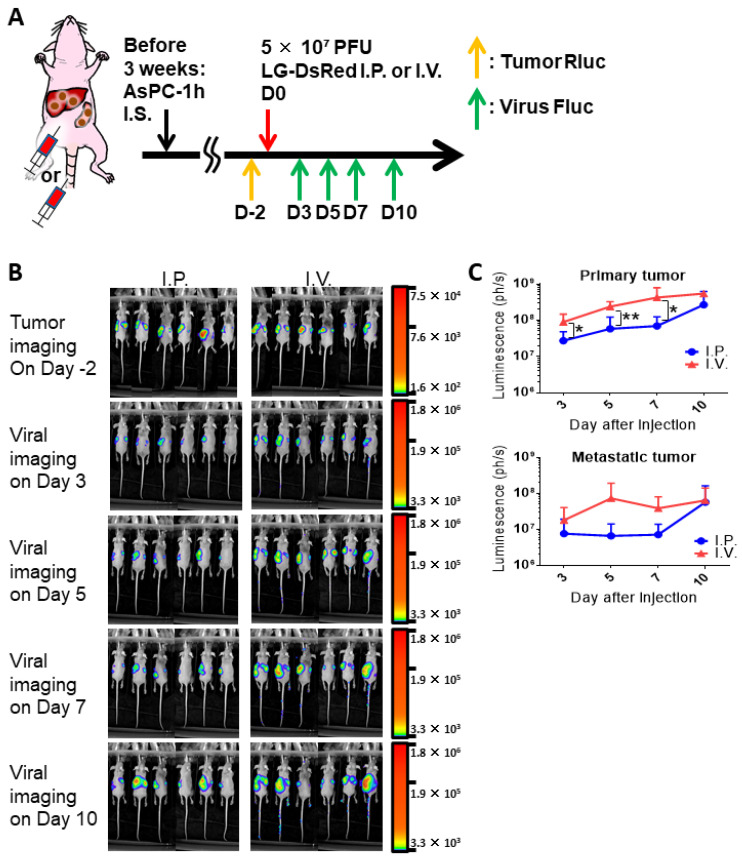
Figure 5.
Comparison of intraperitoneal (I.P.) or intravenous (I.V.) injections of mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent recombinant vaccinia virus (MDRVV) (LG-DsRed) in a mouse model harboring liver metastasis caused by human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. (A) Schematic representation of the study design and timeline of tumor growth and viral distribution. (B) AsPC-1 CD44v9-high cells expressing Renilla Luciferase (Rluc; AsPC-1h) were injected intrasplenically into athymic nude mice and liver metastasis was detected via tumor Rluc luminescence on day 2 before viral treatment. Mice were injected intraperitoneally or intravenously with 5 × 107 PFU of MDRVV (LG-DsRed). Viral replication was detected on days 3, 5, 7, and 10 via firefly luciferase (Fluc) luminescence. (C) Quantification of viral Fluc luminescence in primary splenic and metastatic liver sites was determined from (B). The data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 6). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 (two-tailed unpaired t-test).