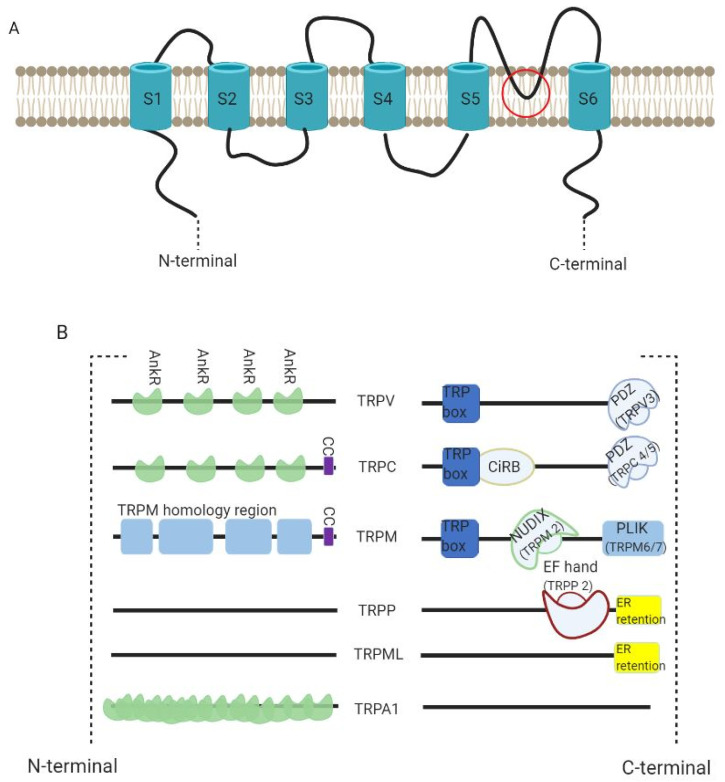
Figure 3.
TRP channel structure. (A) All the channels possess a six-transmembrane (S1 to S6) polypeptide subunits (with a pore-forming re-entrant loop between S5 and S6 as marked in the figure) that assemble as tetramers to form cation-permeable pores. (B) The diversity of the channels is dependent on their C- and N- termini. All TRPV channels have a TRP box at their C-termini and TRPV3 has an additional PDZ binding motif. They have 3–4 Ankyrin repeats (AnkR) in their N-termini. TRPC channels have a TRP box containing the motif EWKFAR plus CIRB (a calmodulin- and inositol triphosphate receptor-binding site). Much like TRPV3, TRPC4/5 have a PDZ binding motif. This subfamily has 3–4 AnkR with an additional coiled-coil domain (CC) in the N-terminus. TRPM channels also have a TRP box in their C-termini. While TRPM2 has NUDIX (a NUDT9 hydrolase protein homologue binding ADP ribose), TRPLM6/7 have PLIK (a phospholipase-C-interacting kinase). In their N-termini, TRPM channels have a CC and a homology region whose functions are unknown. Both TRPP and TRPML have an endoplasmic reticulum retention signal (ER retention) in the C-terminal. TRPP2 also possess a EF-hand (a canonical Ca2+-binding domain) in the N-terminus. TRPA1 channels have a much bigger number of AnkR than TRPV or TRPC. Figure inspired by Clapham D. (2003) [12].