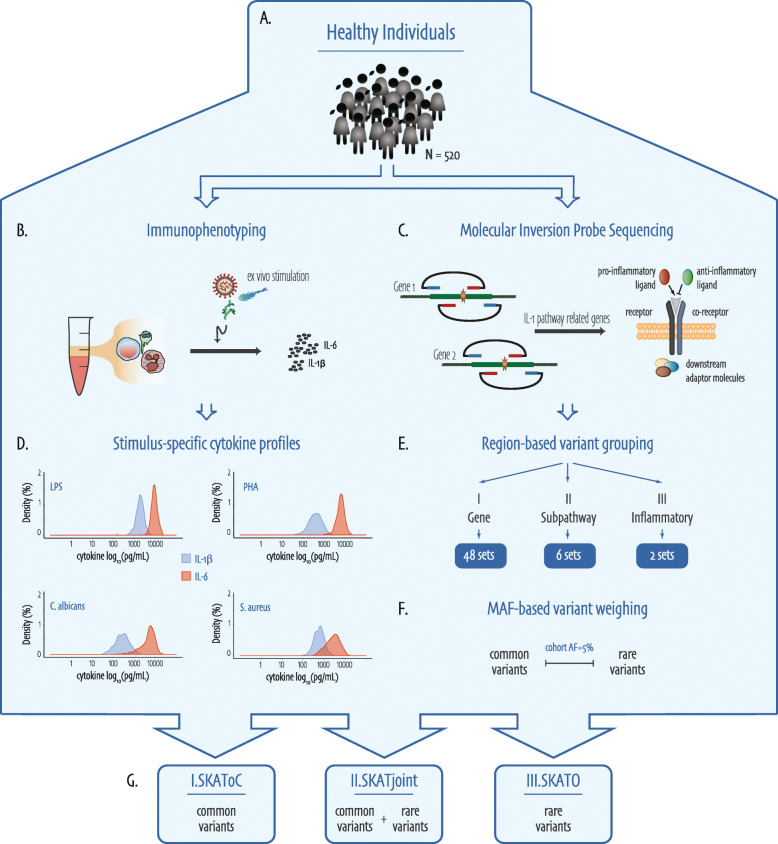
Fig. 1.
Flowchart of the study. Figure orientation from top to bottom. a Blood was extracted from 520 healthy individuals on which (b) extensive immunophenotyping was performed and simultaneously (c) molecular inversion probe sequencing data was produced from the coding regions of 48 Interleukin-1 pathway-related genes. d The resulting cytokine production after stimulation was measured and log-transformed prior to analysis. e The identified variants were grouped over three different levels into sets based on gene-encoded protein function: I. Gene level, with 48 genes; II. Subpathway level, grouping genes into 6 subpathways that represent an immunological cascade in the IL-1-mediated inflammatory response; and III. Inflammatory level, with two groups that distinguish between pro- and anti-inflammatory roles of the respective gene-encoded proteins. f Variants within each set were appropriately weighed based on minor allele frequency (MAF), and common and rare variants were classified based on cohort allele frequency (AF) threshold of 5%. g Finally, variant analysis was performed by the Sequence Kernel Association Test (SKAT) on only common variants (I.SKAToC); common and rare variants combined (II.SKATjoint); and only rare variants using the best combination of the SKAT and burden test (III.SKATO)