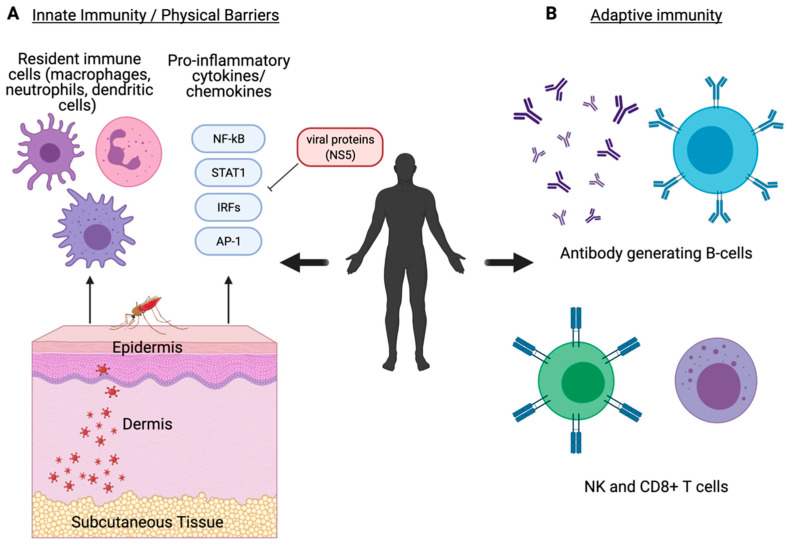
Figure 2.
Innate and adaptive immune signaling in the human system. Humans defend against viral infections using physical barriers, innate immune signaling, and adaptive immune signaling responses. (A) Innate immune responses occur at physical barriers and involve the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines by resident immune cells such as macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells [126,127,128,129,131,132,133]. Components of the innate immune system are well conserved in both mosquitoes and humans. (B) The adaptive immune response primarily involves the generation of specialized and specific antibody-producing B cells, NK cells, and CD8+ T cells [134,135,136,137,138,139,140]. The adaptive immune response is a more evolved form of immunity that is unique to vertebrate organisms. Created with BioRender.com [42].