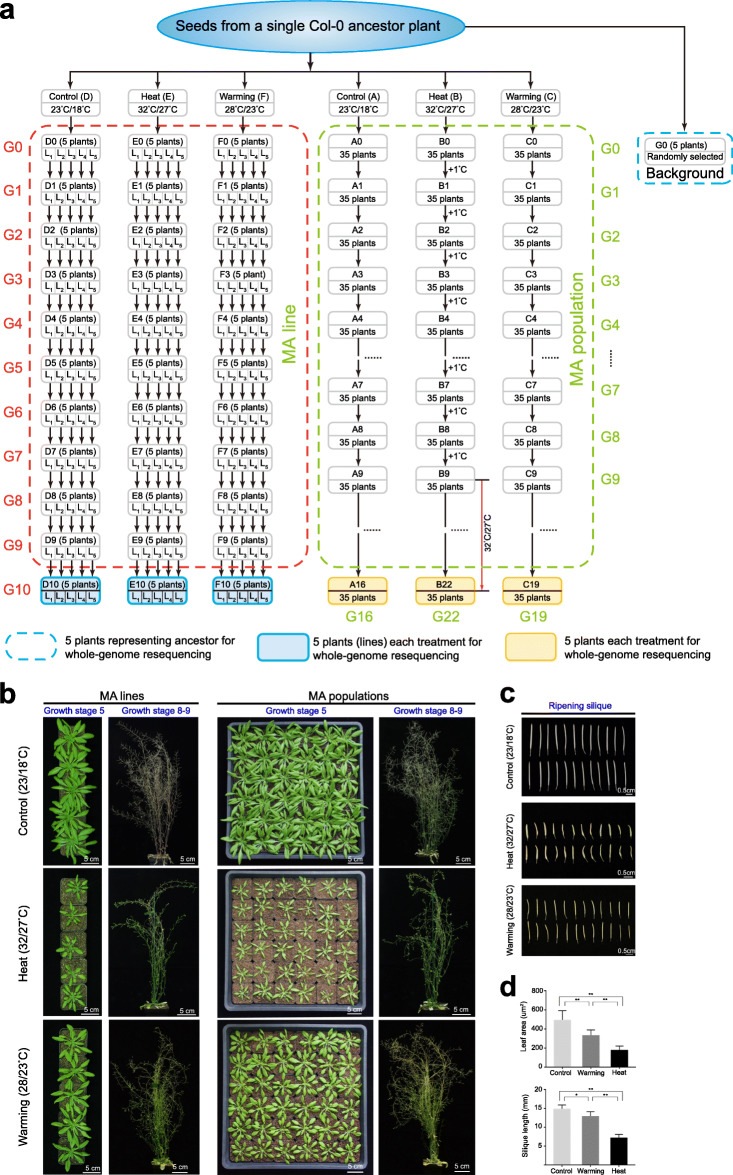
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration and morphological comparison of A. thaliana grown under Control, Heat, and Warming conditions. a Schematic illustration of A. thaliana mutation accumulation (MA) lines and populations. Two MA experiments were conducted in this study (see “Methods”). For MA line experiments, seeds from a single Col-0 ancestor plant were grown independently under Control (D), Heat (E), or Warming (F) conditions for 10 successive generations. Five 10th generation (Generation 10, G10) plants (five MA lines) from each treatment (D10, E10, F10) were used for individual whole-genome sequencing. For MA population experiments, seeds from the same ancestor plant as the MA lines were divided into three groups (~ 35 seedlings per group) and planted under Control conditions (A) for 16 generations, Warming conditions (C) for 19 generations, or Heat conditions (B) for 22 generations [the first 9 generations grown under gradual warming, i.e., increase of 1 °C per generation (from 24/18 °C to 32/27 °C [day/night]); the following 13 generations were grown at constant 32/27 °C]. Five 16th, 22th, and 19th generation plants from each treated population were also randomly selected for sequencing. To maximize coverage and provide progenitor background genetic information (reference genome sequence) for MA experiments, five individuals (G0) were combined for sequencing. Genome-sequenced plants from MA lines and populations are highlighted in yellow- and grey-shaded (blue outline) boxes, respectively; see also Additional file 1: Table S1. b Growth status of MA plants exposed to Control, Heat, and Warming conditions at stage 5 (bolting) and stages 8–9 (silique ripening and senescence). Leaves at stage 5 (major axis ≤ 1 cm) were sampled for DNA extraction and sequencing. Scale bar, 5 cm. c Ripened siliques from the Control, Heat, and Warming treatments. Scale bar, 0.5 cm. d Phenotypic statistics of leaf area and silique length under different temperature treatments. Leaves at stage 5 (bolting) and siliques at stage 9 were measured. The experiments were repeated three times and the data are presented as means ± standard errors of the mean (SEMs; n = 30). Significant differences were revealed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc tests (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. Control or Warming)