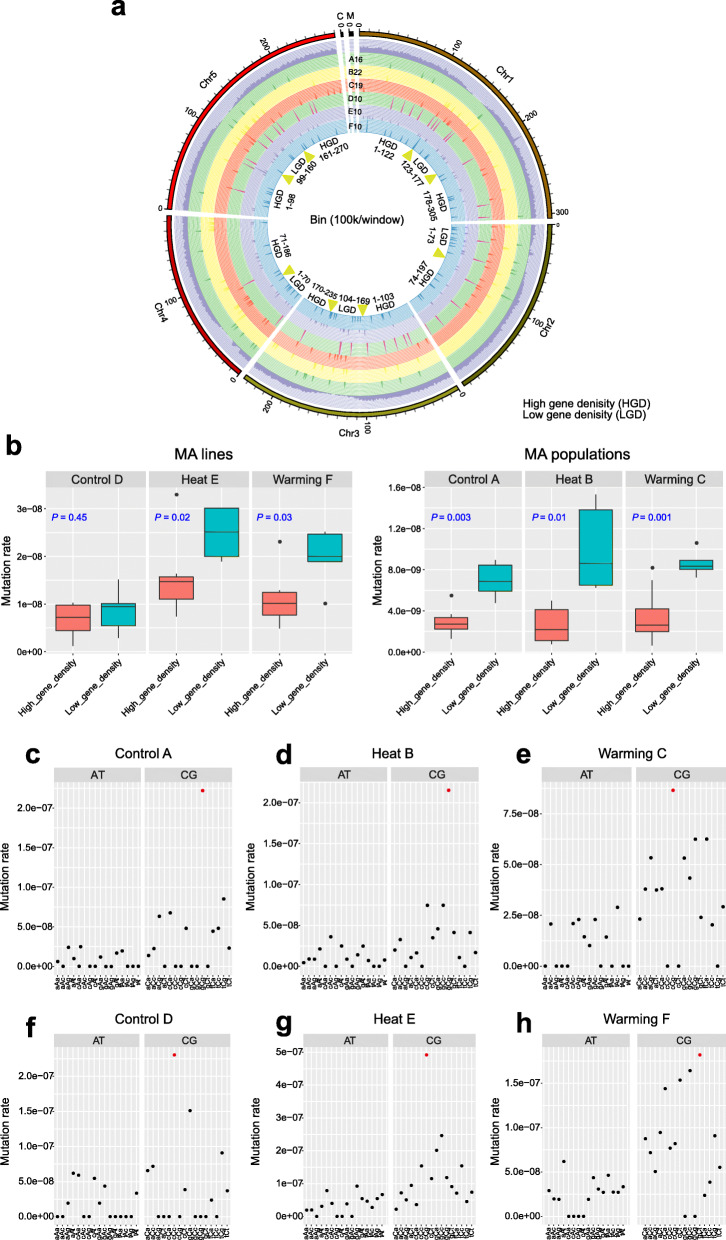
Fig. 7.
Mutational biases of Control, Heat, and Warming lines and populations. Analysis of correlations between gene density and mutation rates across chromosomes in Control, Heat, and Warming lines and populations. a Distribution of mutations across A. thaliana chromosomes shown in a Circos plot. From outer circle to inner circle, the plot shows the chromosomes, genes (purple bars), and mutations in A16 (green bars), B22 (yellow bars), C19 (red bars), D10 (pink bars), E10 (purple bars), and F10 (blue bars). Each chromosome is divided into multiple bins (bin size = 100 kb), which are grouped into high and low gene density regions. b Comparison of mutation rates between regions with high gene density and those with low gene density. Significant differences were revealed using two-tailed Student’s t test (p < 0.05, high vs. low gene density regions). c–h Neighbor-dependent mutation rates at AT and GC bases estimated for the Control, Heat, and Warming MA lines (c–e) and populations (f–h). The trinucleotide context-dependent mutation rate is shown for each treatment. The x axis shows the focal nucleotides (uppercase, mutation site) and immediate flanking nucleotides (lowercase), regardless of strand orientation (e.g., the tAt class includes the overall mutation rate at tAt and aTa sites). For each treatment, the mutation rates of G/C bases were generally elevated relative to those of A/T bases. Red dots indicate significantly elevated mutation rates