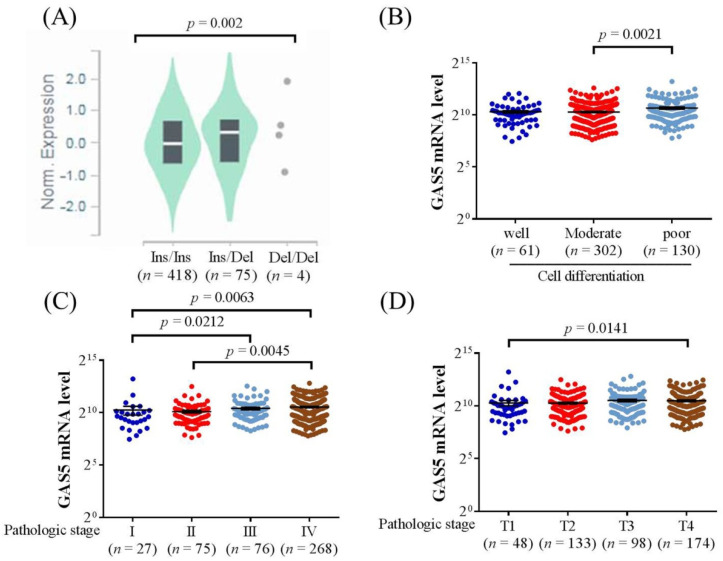
Figure 1.
The relationship between growth arrest-specific 5 expression to growth arrest-specific 5 single nucleotide polymorphism rs145204276 and clinical characters of squamous cell carcinoma. (A) The relationship between the presence of growth arrest-specific 5 single nucleotide polymorphism rs145204276 (Ins/Ins, n = 418; Ins/Del, n = 75; Del/Del, n = 4) and the growth arrest-specific 5 expression in the esophagus mucosa tissues from Genotype-Tissue Expression database. (B) The correlation between the growth arrest-specific 5 mRNA level and the cell differentiation degree of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. (C) The correlation between the growth arrest-specific 5 mRNA level and the cancer stage of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. (D) The correlation between the growth arrest-specific 5 mRNA level and the tumor size of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma from The Cancer Genome Atlas database.