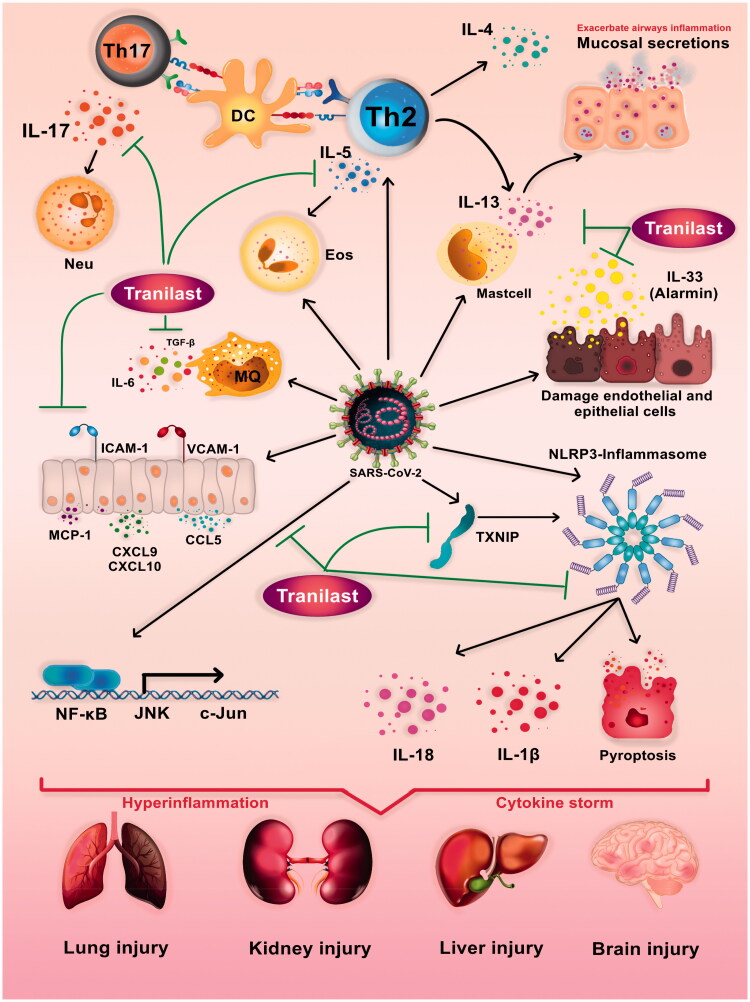
Figure 1.
Putative roles of Tranilast in modulating immune response and Potential mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-induced immunopathology. SARS-CoV2 leads to dysregulation of adaptive and innate immune responses resulting in severe inflammation, cytokine storm and multiple organ dysfunction syndromes. Hyperactivity of inflammasome and dependent pathways, overexpression of chemokines and adhesion molecules, overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines, aberrant differentiation of CD4+ T-lymphocytes, and destructive role of Th17 and Th2 are all key factors in COVID-19 immunopathogenesis. Tranilast has the potential to prevent the exacerbation of COVID-19 by affecting the different pathways such as NLRP3 inflammasome (NLRP3, Caspase1, TXNIP), signaling pathways (NF-κB), cytokines (IL-33, IL-5, IL-17, IL-13, TGF-β), and chemokines (CCL5, CXCL9, CXCL9) and cell adhesion molecules (ICAM1).