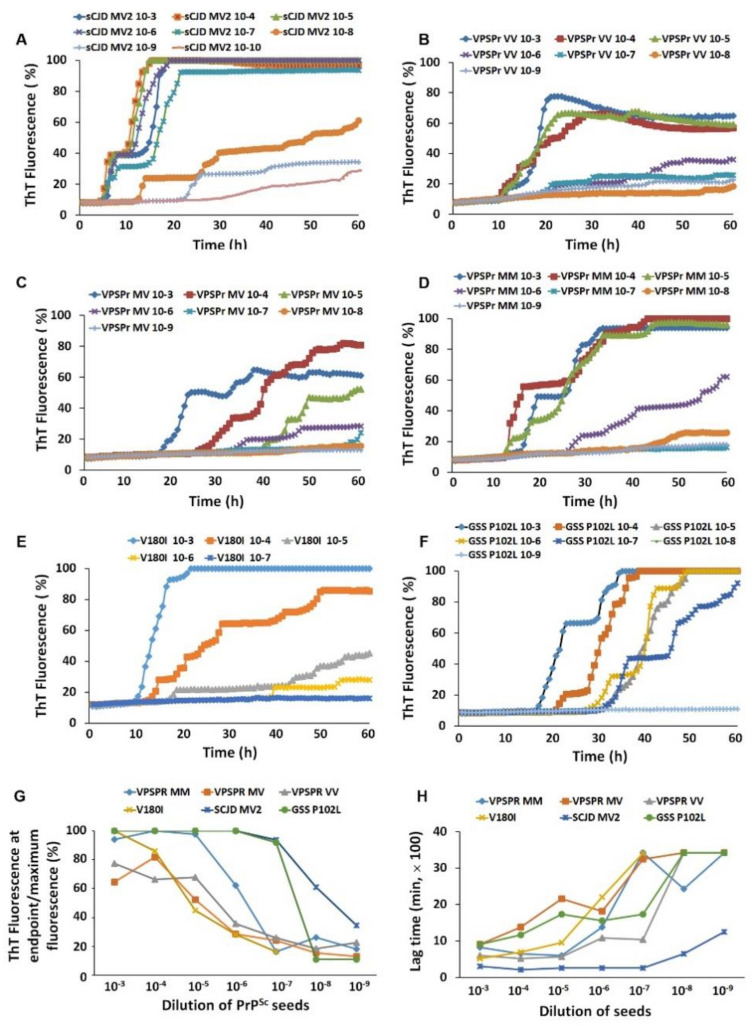
Figure 7.
Comparison of brain prion-seeding activity between VPSPr and other prion diseases by RT-QuIC assay. PrPSc-seeding activity was detected with brain homogenates of VPSPr129MM, VPSPr129MV, VPSPr129VV, fCJDV180I, GSSP102L, or sCJDMV2 as a seed by RT-QuIC assay with recombinant hamster PrP90–231 as a substrate. (A): sCJDMV2 (n = 1, repeating three times); (B): VPSPr129VV (n = 3); (C): VPSPr129MV (n = 3); (D): VPSPr129MM (n = 2); (E): fCJDV180I (n = 3); (F): GSSP102L (n = 3). (G): Maximal ThT fluorescence at endpoint of PrPSc from sCJDMV2, VPSPr129MM, VPSPr129MV, VPSPr129VV, fCJDV180I, and GSSP102L as RT-QuIC seeds. (H): Lag time of PrPSc-seeding activity with brain homogenates from sCJDMV2, VPSPr129MM, VPSPr129MV, VPSPr129VV, fCJDV180I, and GSSP102L as RT-QuIC seeds.