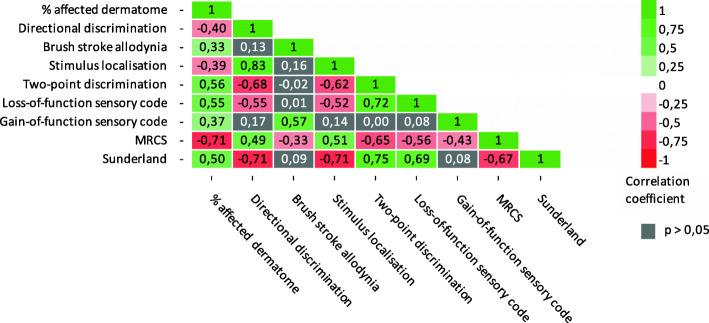
Fig. 1.
Correlation between objective neurosensory measurements. Correlation coefficients of significant positive correlations (P < 0.05) are shown in green. Correlation coefficients of significant negative correlations (P < 0.05) are shown in red. Non-significant correlations (P < 0.05) are displayed in grey. Neurosensory tests consisted of percentage of affected dermatome, directional discrimination, the presence of brush stroke allodynia, stimulus localization, two-point discrimination, sensory phenotype loss- and gain-of-function, MRCS, and Sunderland score