Fig. 6.
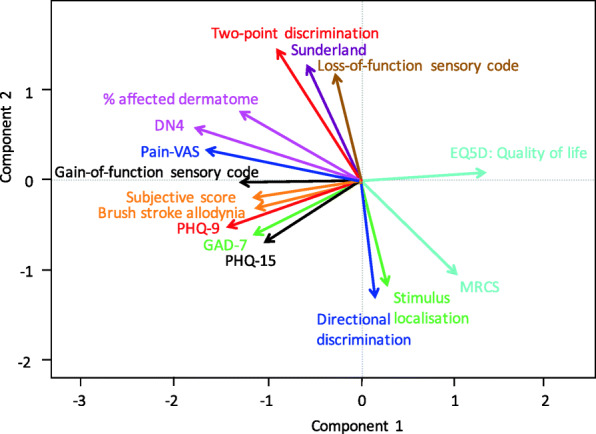
Biplot of all objective and subjective neurosensory measurements. An acute angle indicates a positive correlation. A 90-degree angle indicates no correlation between the two variables, and an obtuse angle indicates a negative correlation. There was a negative correlation of quality of life with gain-of-function sensory code, brush stroke allodynia, and percentage of affected dermatome. In addition, the other questionnaire scores (PHQ-15, GAD-7, PHQ-9, subjective score, Pain-VAS, and DN4) correlated positively with sensory gain-of-function, brush stroke allodynia, and percentage of affected dermatome. Little to no correlation was identified between the different questionnaire scores and the objective measurements of stimulus localization, directional discrimination, two-point discrimination, Sunderland score, and sensory loss-of-function
