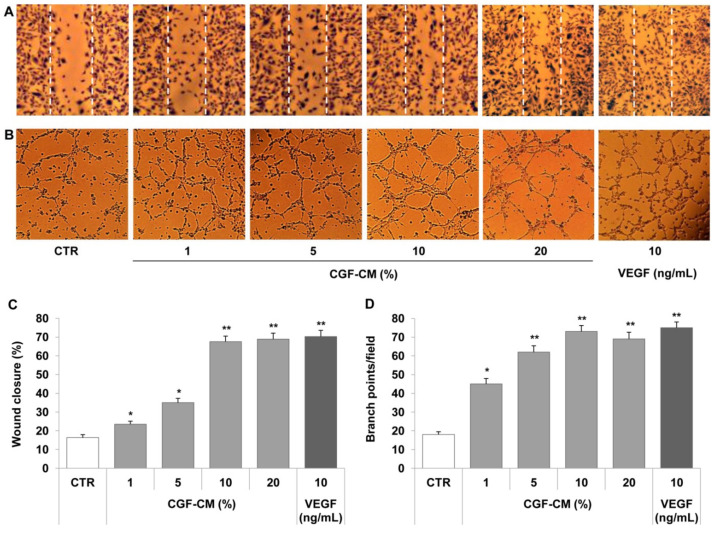
Figure 2.
CGFs promote endothelial cell migration and tube formation. A scratch wound was performed on endothelial monolayers of HMEC-1 that were stimulated with CGF-CM (1%, 5%, 10% or 20%) for 16 h (A). Cell migration was quantified and monitored under phase-contrast microscopy (C). HMEC-1 cells were plated onto a three-dimensional collagen gel (Matrigel) surface and then stimulated with CGF-CM (1%, 5%, 10%, or 20%) or VEGF (10 ng/mL) for 16 h (B,D). Tube formation was monitored under phase-contrast microscopy, photographed, and analyzed. Images are representative of cell migration (A) and capillary-like tube formation (×100 magnification) (B). Data are representative of three independent experiments, expressed as means ± SD, and presented as percentage of wound closure (C) and branch points per field (D). Each experiment consisted of four replicates for each condition. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. control (CTR).