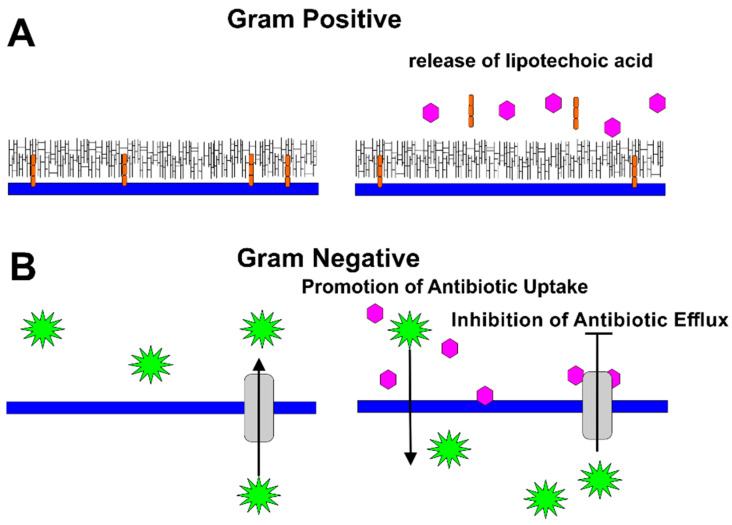
Figure 4.
Mechanisms by Which Catechins Potentiate Antibiotics. (A) In gram-positive bacteria, catechins (pink) mediate the release of lipoteichoic acid (orange), weakening the cell wall of the bacteria. (B) In gram-negative bacteria, catechins (pink) disrupt the packing of the outer membrane, increasing permeability of the antibiotics (green). In addition, catechins were observed to inhibit the activity of bacterial efflux pumps, thus limiting antibiotic export by the bacteria.