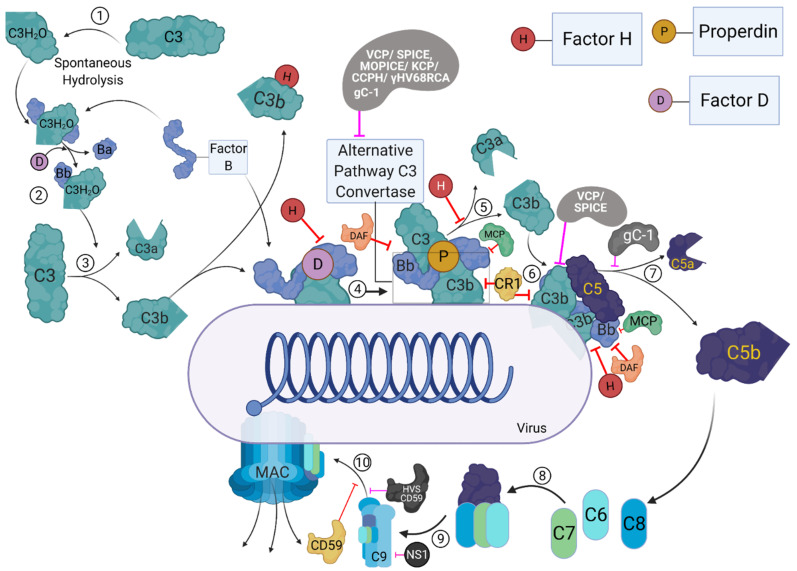
Figure 2.
The activation and regulation of the alternative pathway and its targeting by virally encoded molecules. During the process of alternative pathway (AP), native C3 by H2O is spontaneously hydrolysed, resulting in the formation of C3b like C3 [C3(H2O)] (1). C3(H2O) can bind to factor B (FB), and upon cleavage by factor D (FD), which forms the initial AP-derived C3 convertase (2). The C3 convertase can cleave C3 into C3b and C3a (3). The C3b then binds to the viral surfaces, and trigger the formation of surface bound C3bBb, with the involvement of FB and FD (4). The surface bound C3bBb can then initiate the amplification loop of the AP (5), causing deposition of C3b molecules on to viral surfaces. C3b can combine with pre-existing AP-derived C3 convertase, which leads to the formation of C5 convertase (6). C5 convertase cleaves C5 into C5b and C5a (7). C5b further interacts with C6 and C7 to form C5b-7 (8), which can bind to the surfaces of viruses, while C5a acts as an anaphylatoxins. C5b-7 then binds to C8 which can generate C5b-8 that penetrates the membrane (9). Finally, the C9 binds to C5b-8, resulting in MAC formation (10). The activation steps are regulated at different steps by host complement regulators such as complement receptor 1 (CR1; CD35), membrane cofactor protein (MCP, CD46), decay-accelerating factor (DAF; CD55), factor H (FH), and CD59. Viral proteins that target these pathways are: Vaccinia virus complement control protein (VCP), Smallpox inhibitor of complement enzymes (SPICE), Monkeypox inhibitor of complement enzymes (MOPICE), Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus inhibitor of complement activation (KCP), Murine gamma-herpesvirus 68 regulator of complement activation (γ-HV68 RCA), Herpesvirus saimiri complement control protein homologue (CCPH), Herpesvirus saimiri CD59 homologue (HVS CD59), Flavivirus non-structural protein 1 (NS1), and HSV-1 glycoprotein C (gC-1). These viral proteins are identified as black/grey proteins with white text, and pink inhibitory arrows mark the regulator they inhibit.