Figure 1.
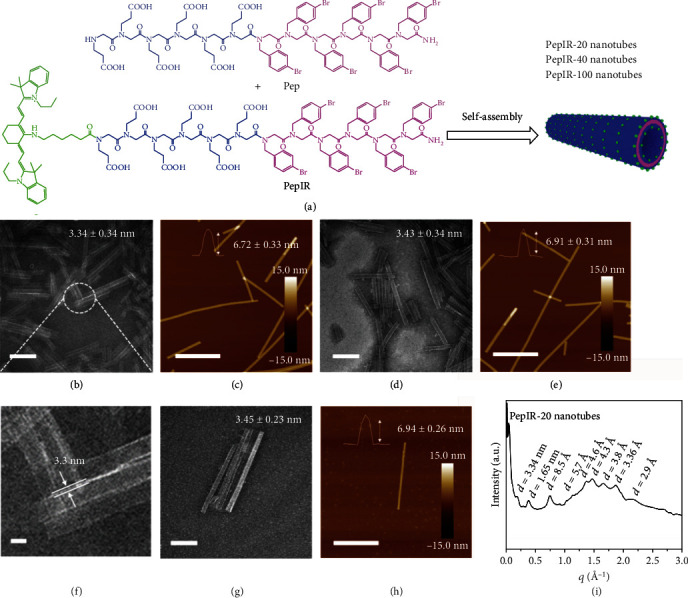
Characterizations of PepIR nanotubes: (a) structures of Pep and PepIR and the scheme showing the self- or coassembly into PepIR nanotubes with a tunable density of IR780 dyes. (b) TEM image of PepIR-20 nanotubes coassembled from 20% PepIR and 80% Pep (scale bar, 200 nm). (c) Ex situ AFM image of PepIR-20 nanotubes (scale bar, 1.0 μm). The top inset is the height of PepIR-20 nanotube. 20 nanotubes were analyzed for obtaining the height distribution. (d) TEM image of PepIR-40 nanotubes coassembled from 40% PepIR and 60% Pep (scale bar, 200 nm). (e) Ex situ AFM image of PepIR-40 nanotubes (scale bar, 1.0 μm). The inset is the height of PepIR-40 nanotube. 20 nanotubes were analyzed for obtaining the height distribution. (f) The high-resolution TEM image showing the wall thickness of nanotubes in (b) (scale bar, 10 nm). (g) TEM image of PepIR-100 nanotubes assembled from 100% PepIR (scale bar, 200 nm). (h) Ex situ AFM image of PepIR-100 nanotubes (scale bar, 1.0 μm). The inset is the height of PepIR-100 nanotube. 20 nanotubes were analyzed for obtaining the height distribution. (i) XRD spectrum of PepIR-20 nanotubes. The formula of d = 2π/q was used to calculate the values above each peak.
