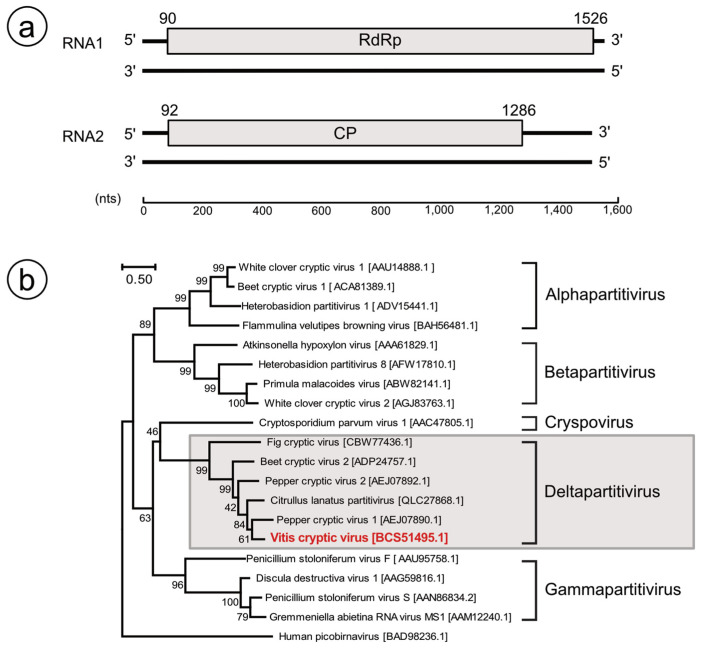
Figure 3.
(a) Proposed partial genome organization of Vitis cryptic virus (VCV). Open reading frames are presented as gray boxes. RdRp: RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, CP: Coat protein. Numbers above gray boxes indicate start/end nucleotide positions of open reading frames. (b) Phylogenetic tree showing the deduced amino-acid sequence of the RdRp gene of VCV showing its position with members of the Deltapartitivirus genus. The evolutionary history was inferred using the maximum likelihood method and the JTT matrix-based model. The tree with the highest log likelihood (−23,194.31) is as presented. Percentages of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together are shown next to the branches. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying Neighbor-Join and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the JTT model and then selecting the topology with superior log likelihood values. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. There were 841 positions in the final dataset. The human picobirna virus was used as an outgroup.